Action Potential
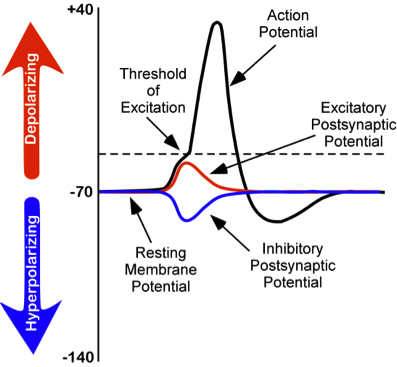
An action potential is an all-or-nothing response (i.e. there is no in-between response) that occurs when there is a change in the charge or potential of the cell from its resting membrane potential (-70 mV) in a more positive direction, which is a depolarization.
Link:
There is a specific membrane potential that the neuron must reach to initiate an action potential. This membrane potential, called the threshold of excitation, is typically around -50 mV. If the threshold of excitation is reached, then an action potential is triggered.
How Action Potential is Initiated
Action potential is initiated through postsynaptic potentials. There are 2 kinds:
- Excitatory postsynaptic potentials (EPSPs): a depolarizing current that causes the membrane potential to become more positive and closer to the threshold of excitation; or
- Inhibitory postsynaptic potentials (IPSPs): a hyperpolarizing current that causes the membrane potential to become more negative and further away from the threshold of excitation.