Error
Three Sources of Error
True error: Mistakes made in the measurement.
- Ex: Experimenter reading a scale on a measurement incorrectly.
Random error: Result from limitations in the precision of the measurements.
Systematic error: Result from some bias in the way that the quantity is being measured.
- Ex: Measuring a current with a ammeter that is not properly calibrated.
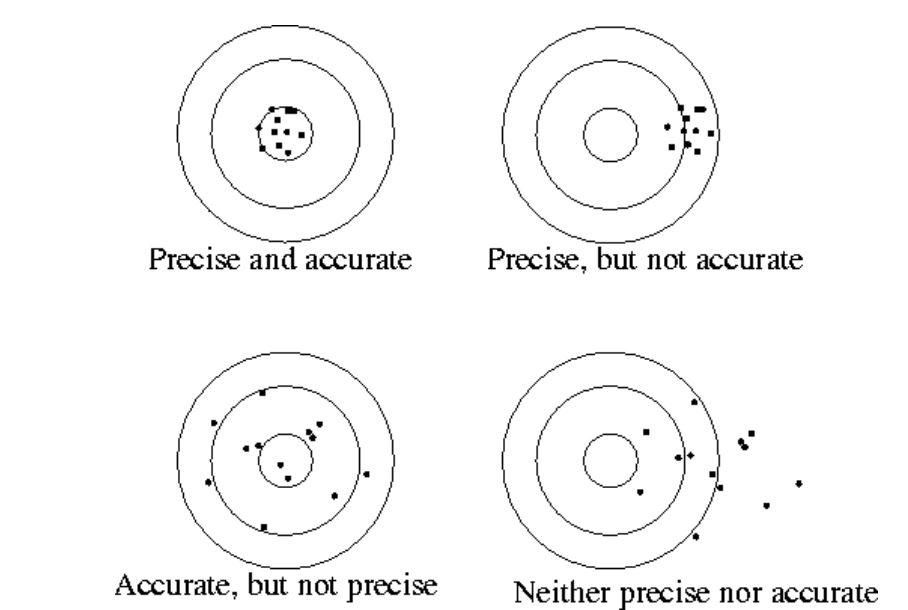
Accuracy vs Precision
Accuracy: How close the measurement is to some quantity.
Precision: Measure of how close repeated measurements are to one another.
CS370
Absolute Error
When we obtain a computed result x of some calculation and we wish to discuss its relationship with the correct mathematical result , we can measure either the absolute error:
Relative Error
The relative error is given by