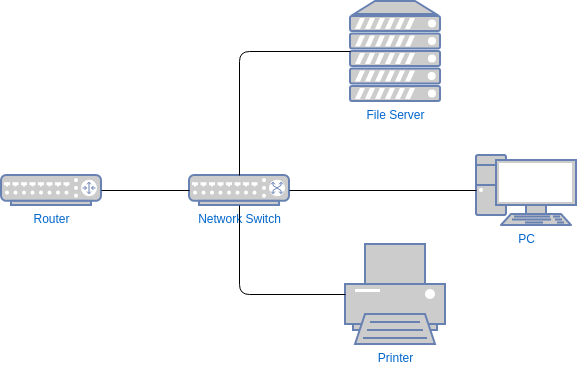
Network Switch
Network switches have the primary function to store and forward packets. Unlike a Network Hub, a switch is intelligent. It reads the incoming data and figures out where to forward it. Reduces unnecessary traffic onto the network.
Network Hub
Hubs and switches are used to create networks.
Hubs and switches are used to exchange data within a LAN. Not used to exchange data outside their own network.
Resources
Router are sometimes used interchangeably with this word, they play the same role.
Hubs and switches do not read IP addresses.
Router vs. switch?
A switch operates within a single network to connect devices (based on MAC addresses), while a router routes data between different networks (assigns local IP addresses).
Types of Switch (L2 vs. L3)
Layer 2 switches offer limited to no routing capabilities within network segments such as VLANs. Layer 3 switches offer routing between different network segments
- L2 Switches (Layer 2): Operate on the data link layer. They use MAC addresses to forward data to the correct destination within a LAN.
- L3 Switches (Layer 3): Operate on the network layer. They use IP addresses to make routing decisions, enabling communication between different subnets and VLANs.
Isn't a L3 Switch just a Router then?
Routers are designed for inter-network communication, while Layer 3 switches are typically used for intra-network routing.
Network Bridge
Same thing?
- Network Switch: A hardware device that connects multiple computers within one local area network (LAN). It uses MAC addresses to forward data frames to specific ports.
- Network Bridge: A device or software that connects two or more network segments, making them function as a single network. It filters traffic, forwarding only the data frames that are needed to cross the bridge.
A Linux bridge is a kernel module that behaves like a network switch, forwarding packets between interfaces that are connected to it
Resources