Operational Amplifier (Op-Amp)
The operational amplifier is an electronic circuit that is widely used in many practical electronic systems such as TV’s, stereos, phones, control systems, medical equipment, etc.
Main Operations of Op-Amp:
- Amplification
- Addition
- Subtraction
- Differentiation
- Integration
- Filtering
- Many more, including non-linear operations
Inverting amplifier?? → this is when the output voltage is inverted (opposite sign).
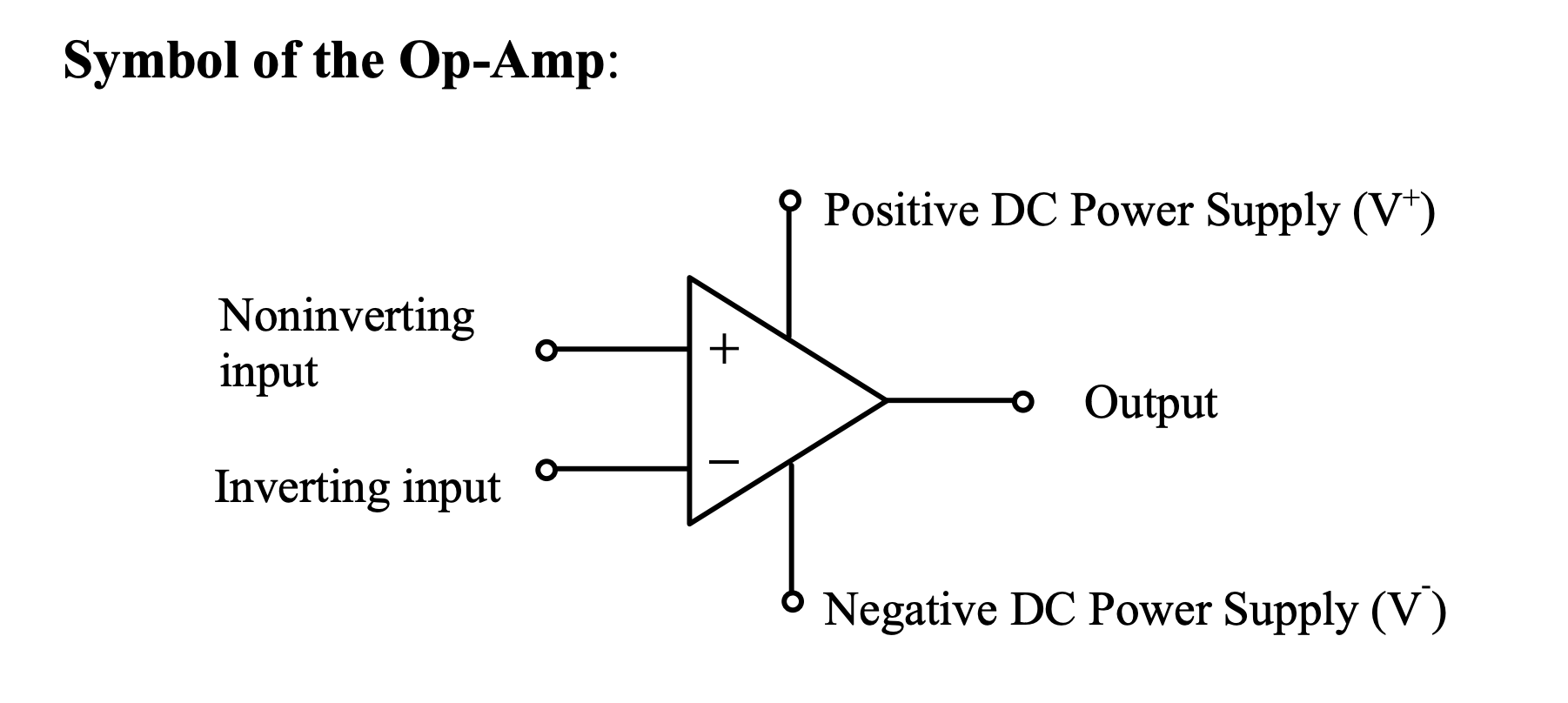
Symbol Conventions Explained
- is positive voltage
- is negative voltage
- is like output voltage
- Positive DC Power Supply ()
- Negative DC Power Supply ()
Other
- is like input voltage, also written as , equal to
We don't draw the power supply inputs of the op amp usually to prevent clutter in the schematic, but it is there.Non-Ideal Op-Amp Model
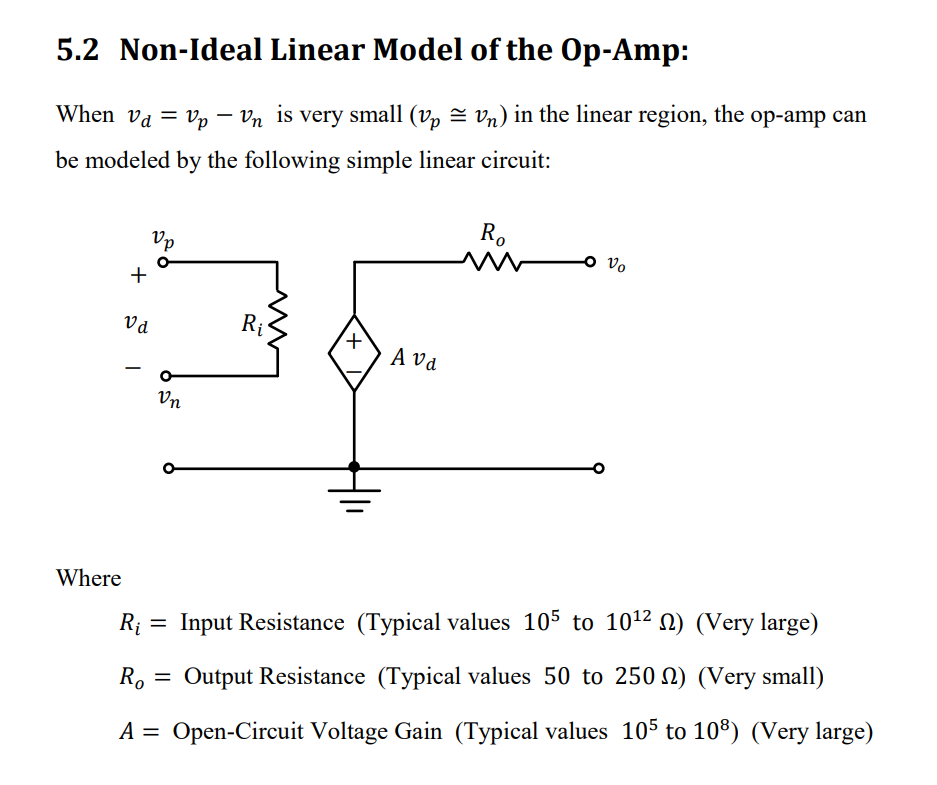
Ideal Op-Amp Model
If we assume it is an ideal op-amp, it makes the analysis of op-amp circuits very easy and quick.
Assumptions
- We assume Input resistance is very large, so
- Voltage gain is very large, so
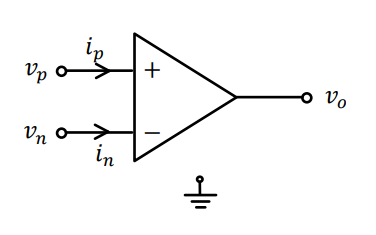
Finding Output voltage
Sometimes, in the question, they might ask to give the output voltage.
This is as simple as , where is the voltage gain.
However, you need to make sure that If it is not met, you use whichever one saturates.
Ex: if you calculate but , then the output saturates at
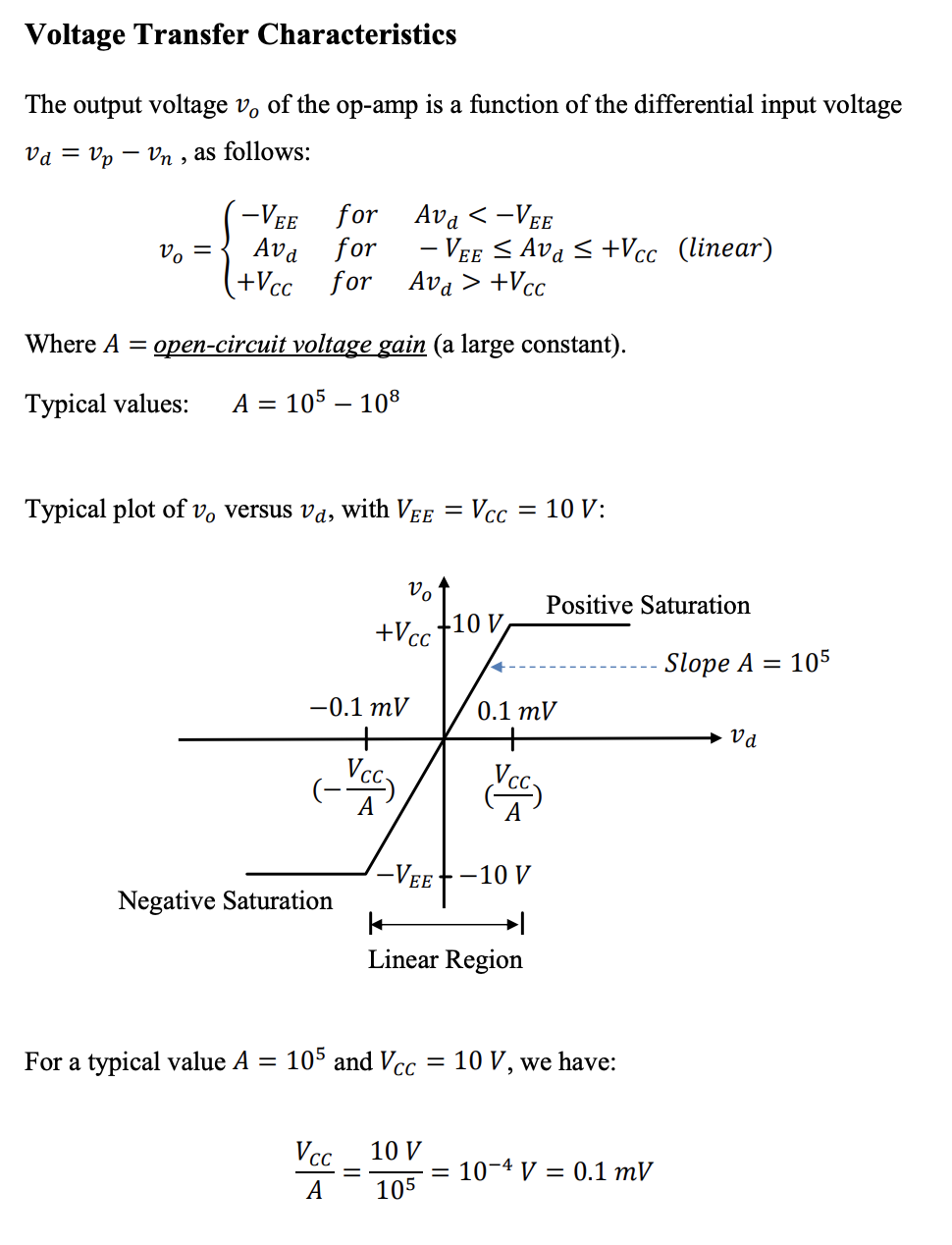
Voltage Transfer Characteristics
The non-ideal/ideal op-amps described above are created based on the properties described below.
I still don’t understand a lot, but I am writing these notes hoping to extend on them in the future.
The Op-Amp only operates at certain voltages. It must satisfy:
This implies that (condition for linear region)
The gain is how much the voltage is gained
represents this slope. Ideally, this slope is infinite so we instantly go from negative saturation to positive saturation.
The reality is represented by the graph below.
title: I don't understand how op-amps work lol #gap-in-knowledge
I still don't understand.
What is the purpose of an op-amp?
I know perfectly well how to solve a circuit assuming that it is an ideal op-amp, but I don't understand why it works.
i.e. how does Voltage gain work? How do we design op-amps with the right voltage gains?Related
Think about the difference between this and Buck Converter / Buck Converter / Boost Converters. There’s several differences as explained in this reddit post.