Secure Shell Protocol (SSH)
The Secure Shell Protocol is a cryptographic network protocol for operating network services securely over an unsecured network.
Make sure to set up your ssh keys, Based on Public-Key Cryptography https://www.ssh.com/academy/
We can ssh from the terminal by running, for example
ssh <username>@bastion.watonomous.ca
To copy files, use scp <source> <destination>
SUPER USEFUL, LEARNED FROM ASHWIN at NVIDIA
Instead of having to write the password every time you SSH, or having to manually copy paste, you can do
ssh-copy-id user@IP
Then, later, you can just
ssh-copy-id user@IP
scp -r /mnt/wato-drive2/perception_datasets/traffic_light_1
BE CAREFUL, this breaks for an existing file if the time does not align properly.
use sshpass to include the password into it.
sshpass -p 'f1tenthUW!' scp /Users/stevengong/Projects/f1tenth_ws/nodes/pure_pursuit/src/pure_pursuit_node.cpp f1tenth-uw@10.42.0.1:f1tenth_ws/src/pure_pursuit/src/pure_pursuit_node.cpp# from local to remote
scp ./e7_floor5_clean.pgm f1tenth-uw@10.42.0.1:f1tenth_ws/src
scp /Users/stevengong/Projects/f1tenth_ws/nodes/pure_pursuit/src/pure_pursuit_node.cpp f1tenth-uw@10.42.0.1:f1tenth_ws/src/pure_pursuit/src/pure_pursuit_node.cpp
scp -r ./video_frames s36gong@trpro-ubuntu1.watocluster.local:/home/s36gong/Musashi-AI
# From remote to local
scp f1tenth-uw@10.42.0.1:f1tenth_ws/<remote_file> .
# For directories, it is the same syntax but add the -r flag
scp -r /path/to/directory user@machine_b_ipaddress:/path/to/destination
scp -r user@machine_a_ipaddress:/path/to/directory /path/to/destination
For WATonomous (with a jump host):
From my computer to remote
scp -i ~/.ssh/id_rsa -o ProxyJump=s36gong@bastion.watonomous.ca -r /path/to/local/folder s36gong@delta-ubuntu2.cluster.watonomous.ca:/path/to/remote/destination
From remote to my hard drive
scp -o ProxyJump=s36gong@bastion.watonomous.ca -r s36gong@delta-ubuntu2.cluster.watonomous.ca:/mnt/wato-drive2/rosbags2/2024 /Volumes/G-DRIVE\ ArmorATD/rosbags
scp f1tenth-uw@10.42.0.1:f1tenth_ws/rrt.rviz .
SSH Command options
Some of the most important command-line options for the OpenSSH client are:
-1Use protocol version 1 only.-2Use protocol version 2 only.-4Use IPv4 addresses only.-6Use IPv6 addresses only.-
-frun thesshcommand to run in the background -Ndo not to execute a remote command.- -C Use data compression
- -c cipher_spec Selects the cipher specification for encrypting the session.
- -D
**[bind_address:]**port Dynamic application-level port forwarding. This allocates a socket to listen to port on the local side. When a connection is made to this port, the connection is forwarded over the secure channel, and the application protocol is then used to determine where to connect to from the remote machine. - -E log_file Append debug logs to log_file instead of standard error.
- -F configfile Specifies a per-user configuration file. The default for the per-user configuration file is ~/.ssh/config.
- -g Allows remote hosts to connect to local forwarded ports.
- -i identity_file A file from which the identity key (private key) for public key authentication is read.
- -J
[user@]host[:port]Connect to the target host through Jump Host -l login_nameSpecifies the user to log in as on the remote machine.-p portPort to connect to on the remote host.vVerbose mode.-X/-xto enable / disable X11 forwarding.
Different SSH Keys
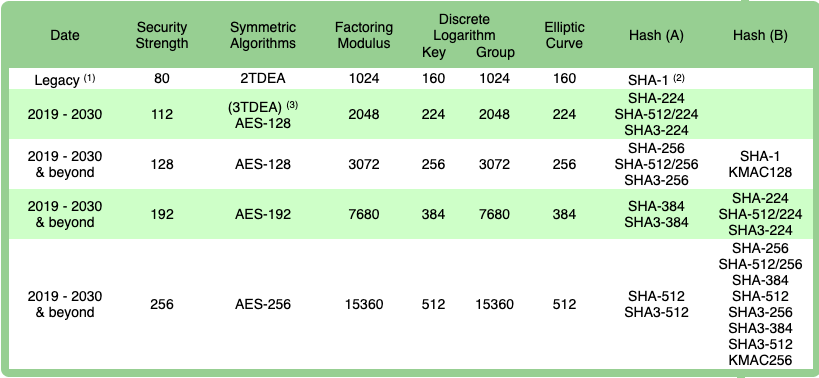 ssh-rsa vs.
ssh-rsa vs.
When it comes down to it, the choice is between RSA 2048/4096 and Ed25519 and the trade-off is between performance and compatibility.
RSA is universally supported among SSH clients while EdDSA performs much faster and provides the same level of security with significantly smaller keys.