XSkill: Cross Embodiment Skill Discovery
They seem to take both human dataset and robot dataset, and do some fine-tuning on it?
Project website:
- Discover
- Transfer
- Compose
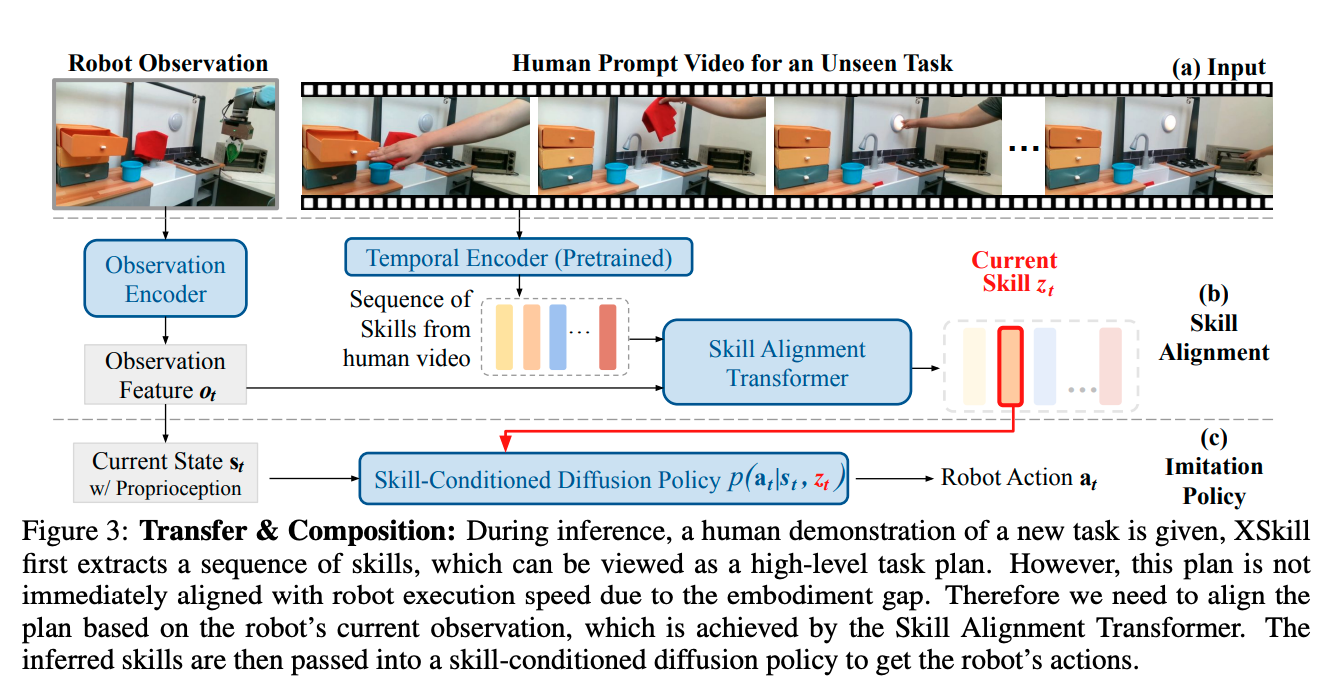
I think what’s cool about this paper is that we don’t need to explicitly split out the episode into sub-skills because when we do the human prompt, we’re able to do this alignment via self-supervised learning.
How do they get this alignment?
- To achieve this alignment, XSkill introduces a set of K learnable skill prototypes ().
- These prototypes act as representative anchors in the continuous embedding space.
- The crucial step is that XSkill forces both the human and robot skill representations to share the same set of prototypes. This constraint means that a video clip showing a robot grasping an object and a video clip showing a human grasping an object must both map to the same anchor point (prototype) in the shared space.
1. Discover
They use sinkhorn-knopp algo for learning a representation invariant to human body
Skills as Prototypes. Once the skill representations are obtained from demonstration videos, XSkill maps representations from all embodiments to a set of K skill prototypes {ck} K k=1, where each is a learnable vector
2. Transfer
Use a skill-conditioned diffusion policy