Data Stream
Learned in CS451.
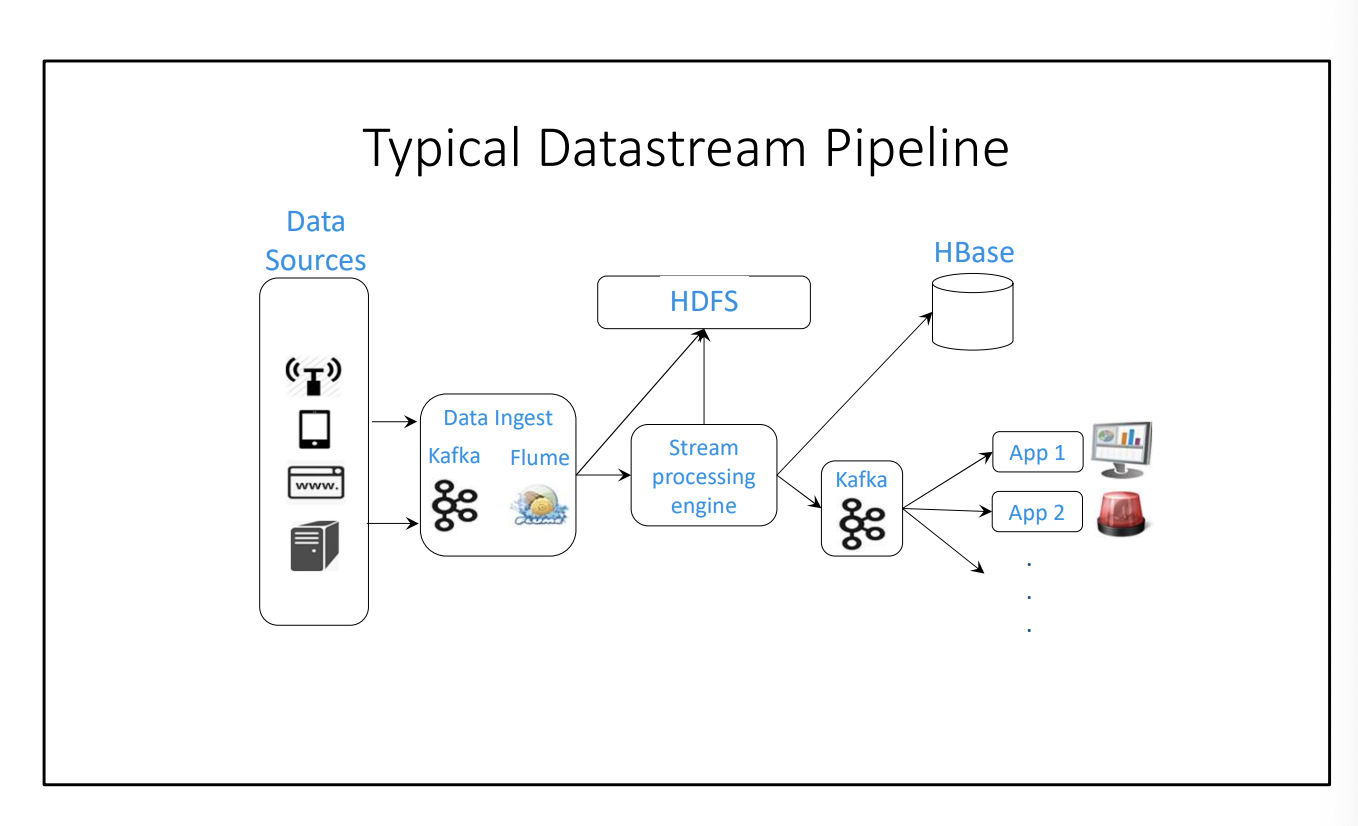
- Apache Kafka – A distributed pub-sub broker designed for resilience and availability
- Apache Flume – A distributed log aggregator (designed for resilience and availability)
- Stream-Processing-Engine – The top of this module
- HBase – Distributed key-value datastore, modelled after Google’s BigTable and built on top of HDFS
A Data Stream
A data stream is a sequence of items (tuples)
- Structured
- Ordered (either a timestamp, or implicitly by arrival time)
- Continuously arriving
- High volume
- Might not be possible to store all of it
- Might not be possible to even examine all of it
The main question is: How do you process a stream of data, when you don’t have all of it?
- The problem is that the “reduce-like” tasks – grouping, aggregating, and joining – rely on having all of the data. How can we define them “continuously?”
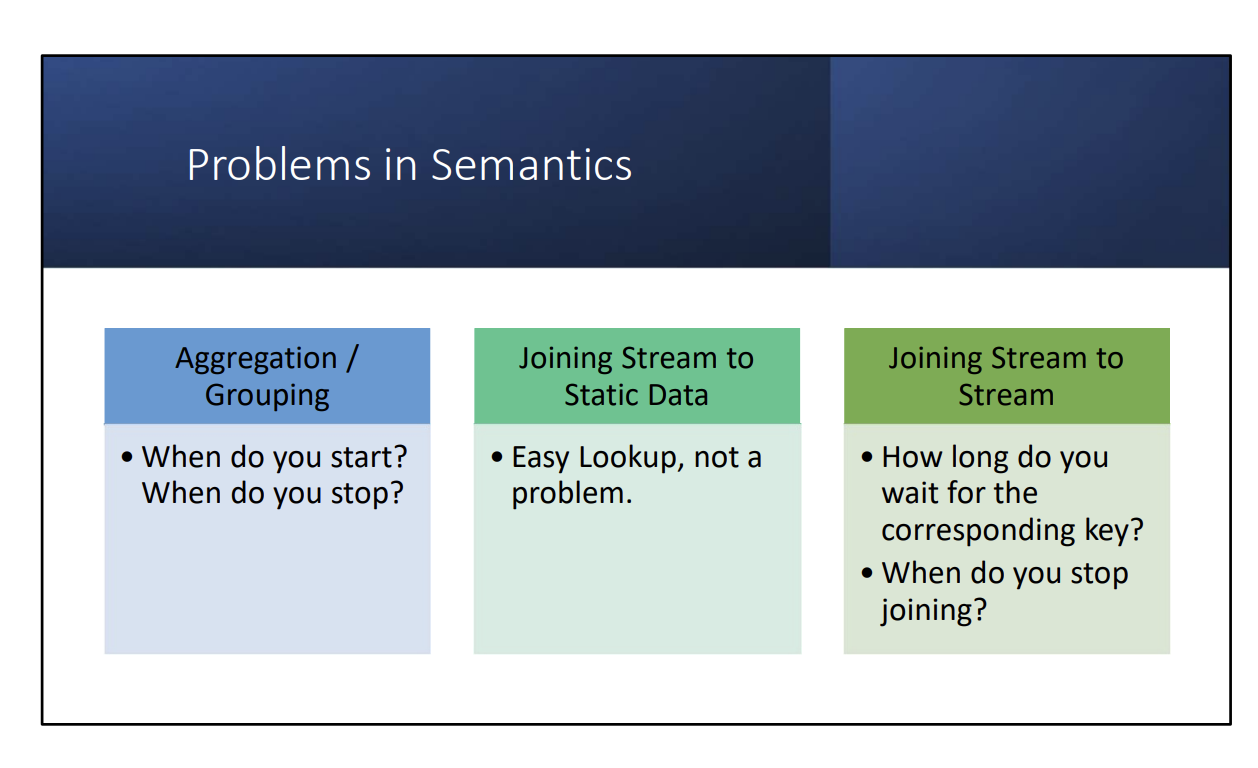
Easy: You can just do your reduce operations over a window.
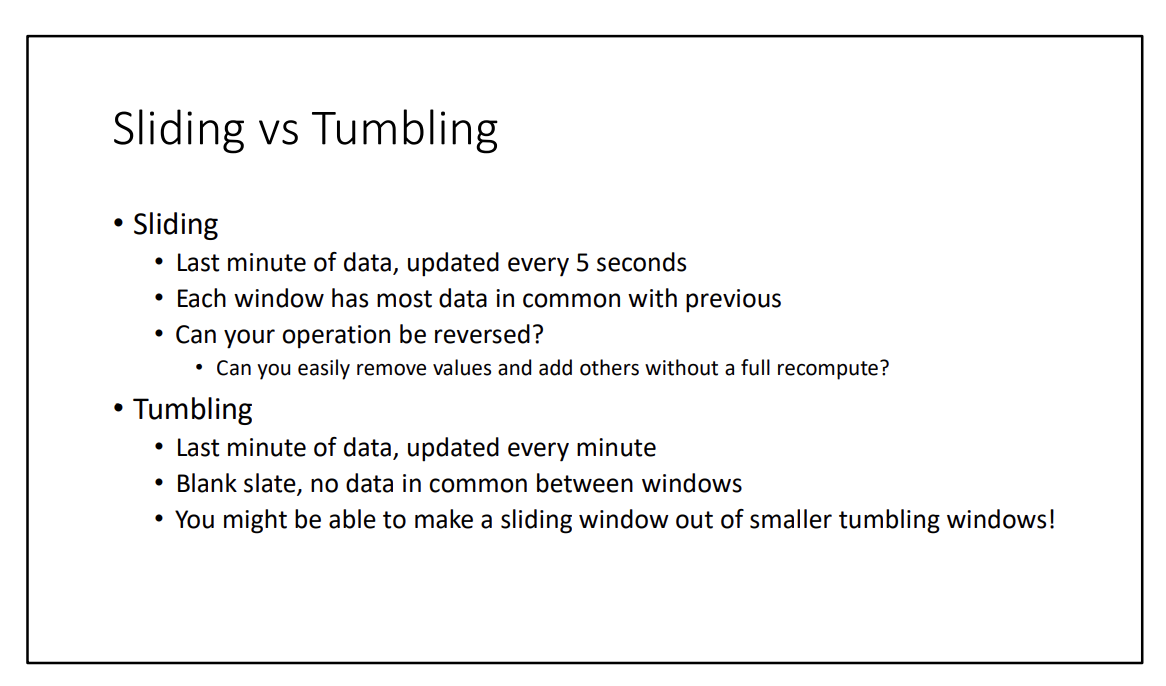
There are 2 implementations:
- Sliding
- Tumbling
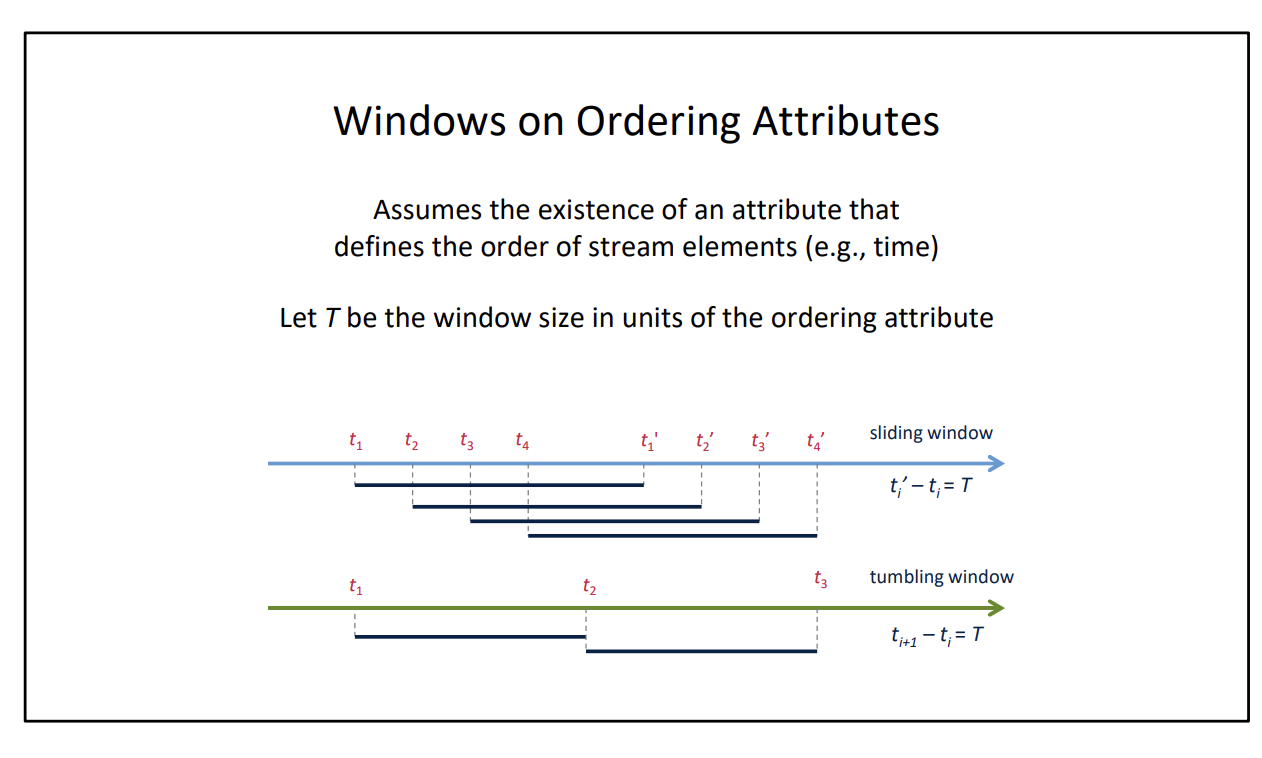
Windows: Define all “reduce-like” transformations for a given window.
There are many ways to window:
- Based on ordering attribute (timestamp)
- Based on counts (last X records)
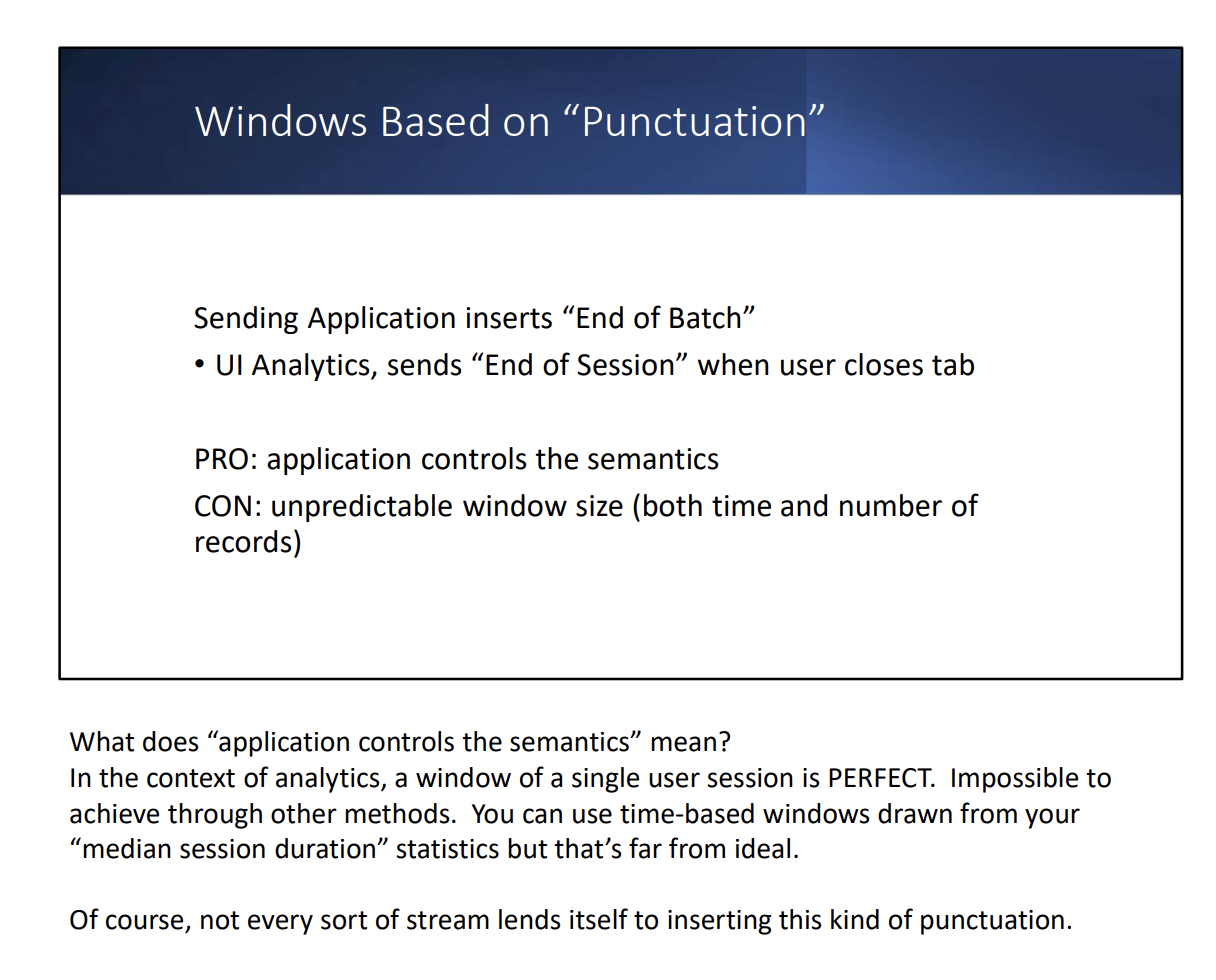
- Based on explicit markers (ex: punctation)
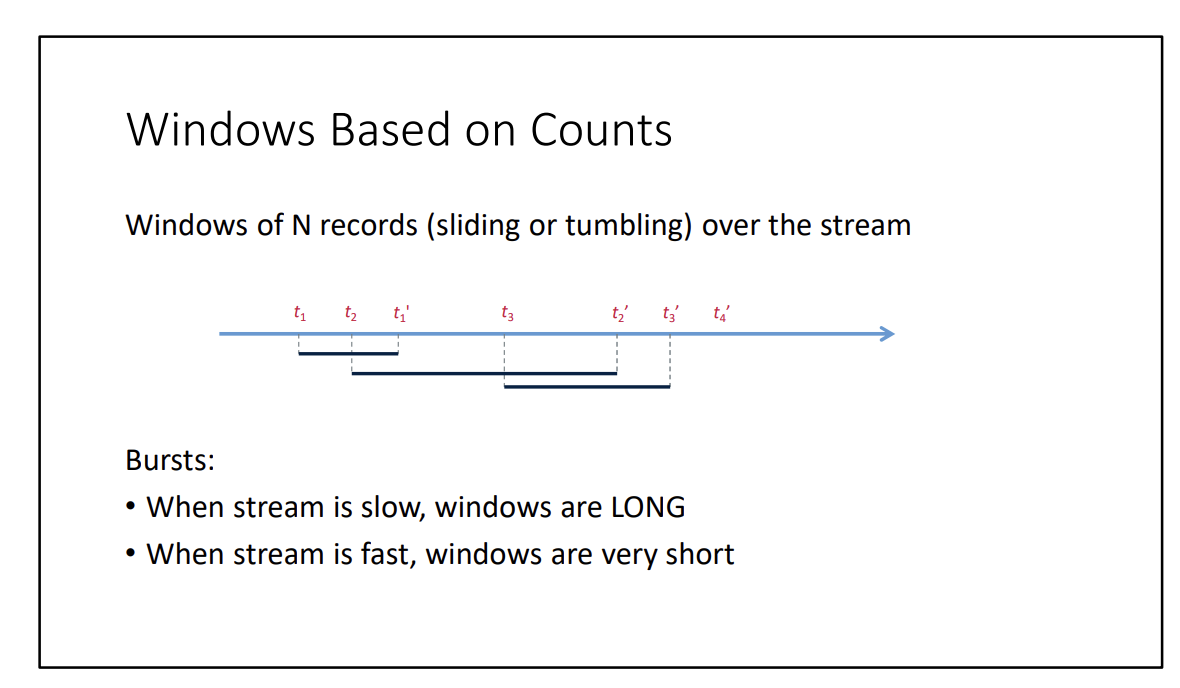
When there is bursty data, you apply Reservoir Sampling.