Data Type
There are 2 categories of data types:
Other things to be aware of:
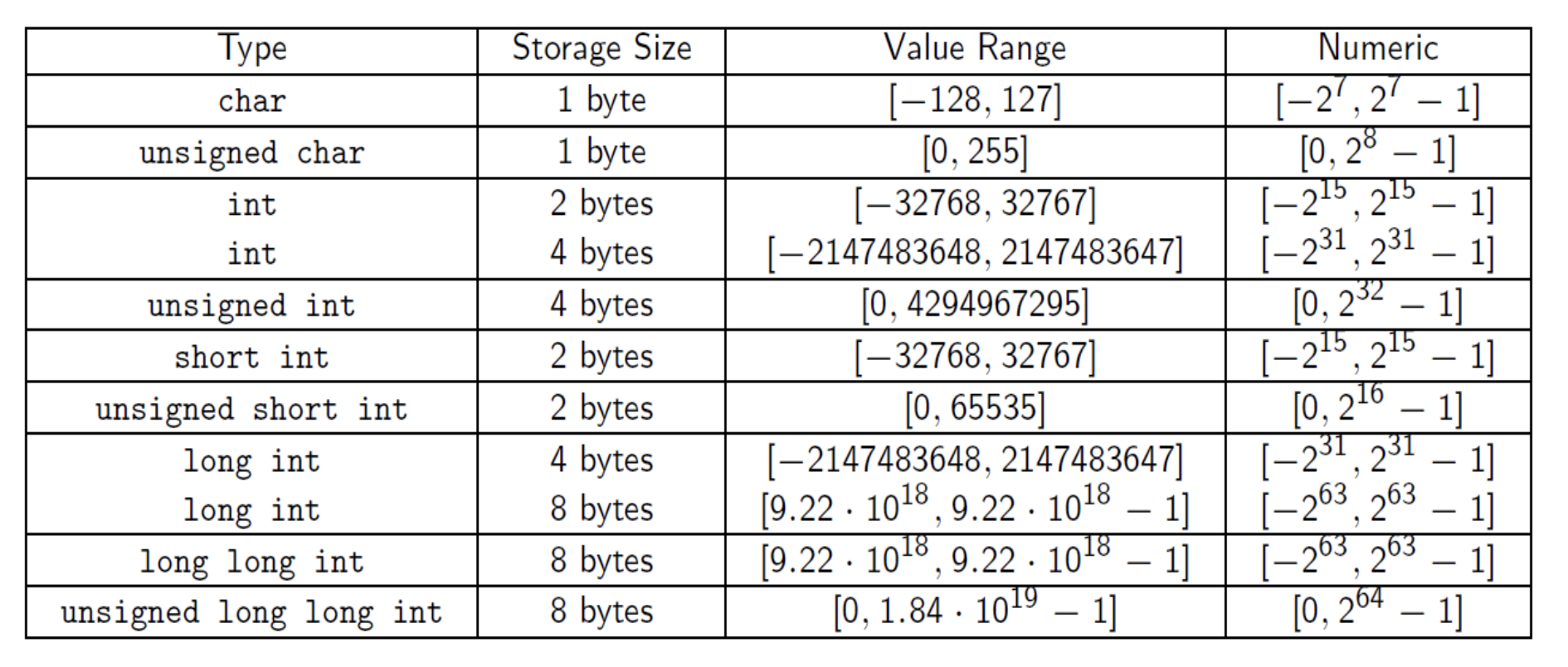 Also see Signed vs Unsigned Numbers.
Also see Signed vs Unsigned Numbers.
Floating Point Numbers
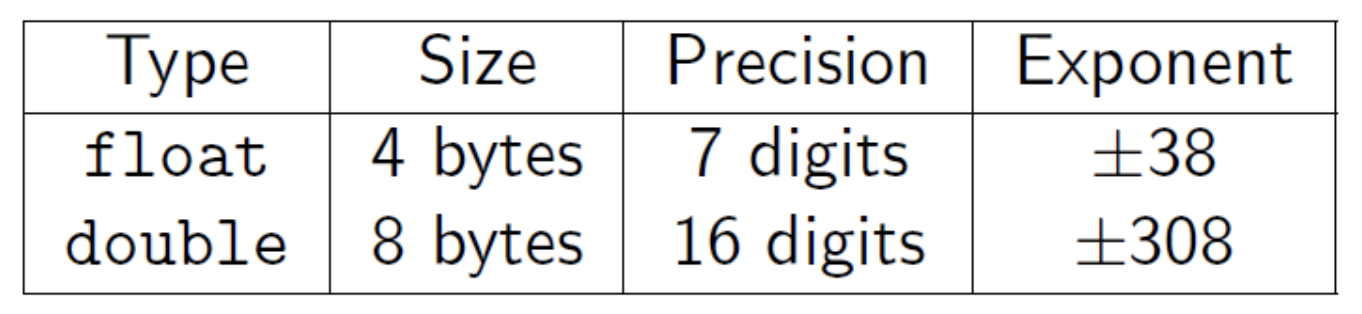
See FP32 (float) and FP64 (double).
Dealing with Floats and the decimals
float val = sqrt(2);
// If you want 12 decimal places
cout << setprecision(12) << fixed << val << endl;Functions you can use:
ceil(5.3) // 6
floor(5.3) // 5
# round() will round to closest integer
round(5.3) // 5
round(5.6) // 6How to Convert Binary Number to Float?
I don’t know. Check this article out. Hemal Shah talked about this to me, about how there is the exponent and the mantissa.
- Update: Since my time an Tesla, I have become expert of floating point, by implementing an internal floating point library.
Data Types From STAT206
This is also the same categorization we do in Machine Learning.
- Categorical
- Ordinal (subtype)
- Numerical
- Discrete
- Continuous
Miscallaneous
Integral Type
An integral type is anything that can be represented by an integer. Ex: Character and String, Enum (C++).