Embedded Systems (Firmware)
See WARG.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=I7kIcpWTulE&ab_channel=SkillLync
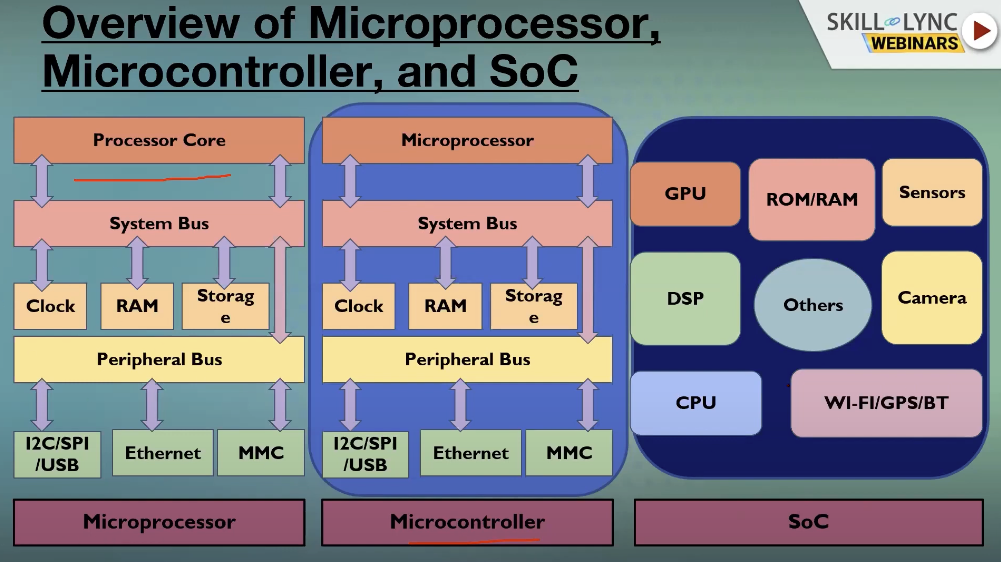
Microprocessor vs. Microcontroller vs. SoC
Microprocessor = IC that contains only a CPU
- Does not contain ROM, RAM, etc. which are necessary to perform a task
- External components are required to perform a task
CPU = microprocessor?
https://download.intel.com/newsroom/kits/40thanniversary/pdfs/What_is_a_Microprocessor.pdf
Microcontroller
- A Single IC mini-computer
- Microcontrollers are complete and self-sufficient
- Have RAM, ROM, Timers, Serial ports
Well suited for compact and embedded device.
SoC
- Advanced version of microcontroller or microprocessor
- Integrates well with advanced peripherals like GPU, WiFI module, or other coproessors
Firmware vs. Software
- Nowadays, it is harder to differentiate
Firmware
- Firmware refers to the software stored in read-only memory such as EPROM, or EEPROM
- Used as a low-level software that operates a specific, single-purpose device like TV, washing machine, A/C
- There is no OS in firmware so it is called bare metal
Firmware Application vs. Firmware Driver
Firmware Driver
- If we make use of any embedded components (like SD card), we need a driver to communicate with it
- It is also called a low-level driver which is written to update and configure specific registers of the peripheral
Firmware Application
- Makes use of the device by calling specific APIs of the firmware driver
- Specifies which register to modify, and the firmware driver will do it
Flash Memory vs. RAM?
- He has the drawing where the data is actually stored in RAM, but the code is stored in flash memory which is executed
Some good questions
- Why is register variable global declaration is not possible?
- Why can’t static variables be declared within a
struct?