Hash Table
A Hash Table stores data with key value pairs without sortedness.
I think this is the most intuitive https://www.tutorialspoint.com/data_structures_algorithms/hash_data_structure.htm
A Hash table consists of a
- Hash Table
- Hash Function
- A strategy for dealing with Hash Collisions
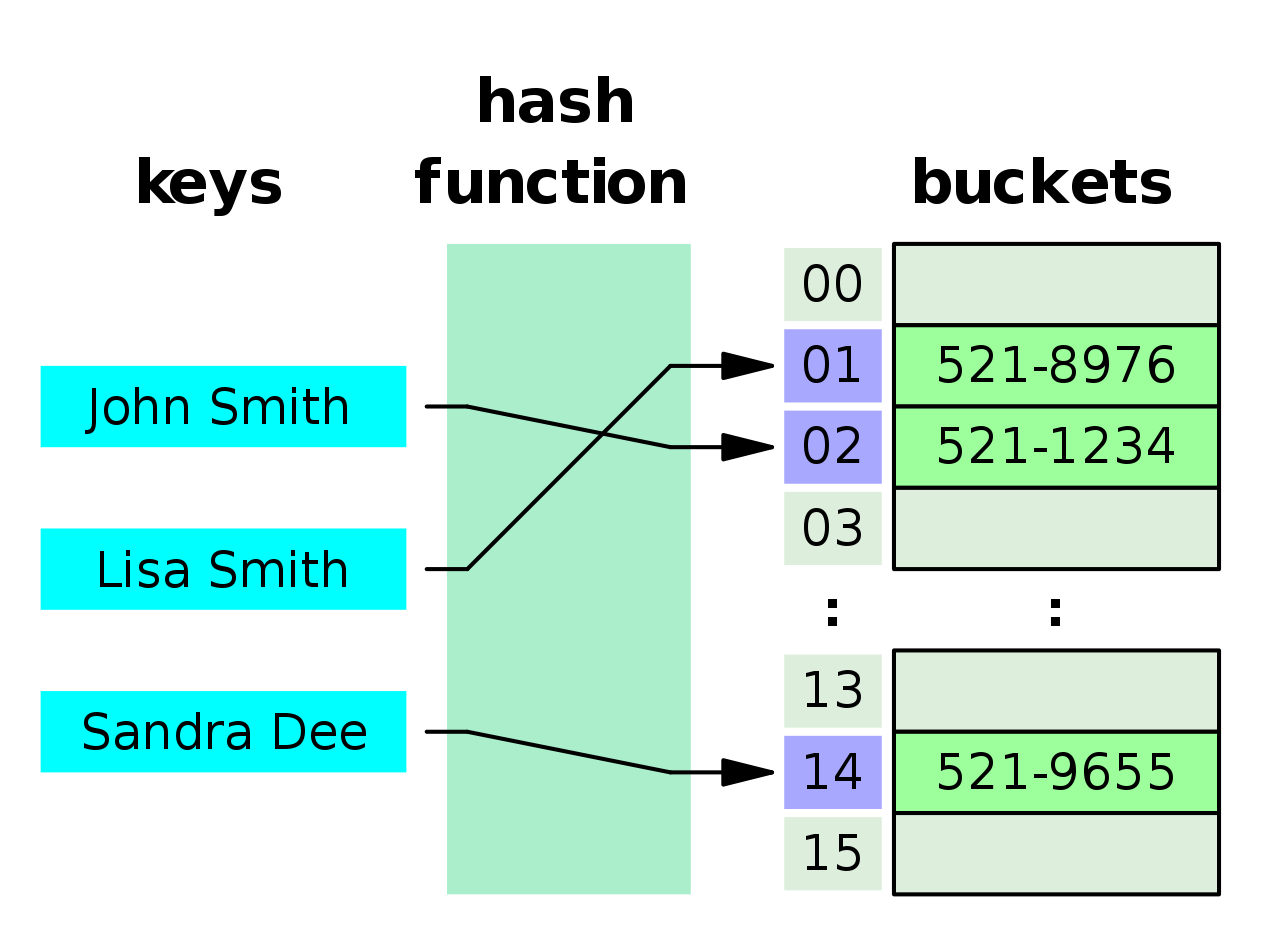
What you need to know
- Designed to optimize searching, insertion, and deletion.
- Hash collisions are when a hash function returns the same output for two distinct inputs.
- All hash functions have this problem.
- This is often accommodated for by having the hash tables be very large.
- Hashes are important for associative arrays and database indexing.
Time Complexity
- Indexing: Hash Tables: or
N/A? - Search: Hash Tables:
- Insertion: Hash Tables:
- Deletion: Hash Tables:
Implementation
Basically, when you explain it in a coding interview, you need to:
- Define a mapping from your custom class to some unique key as an index
- the original key which map to some index buckets, which would store the actual values
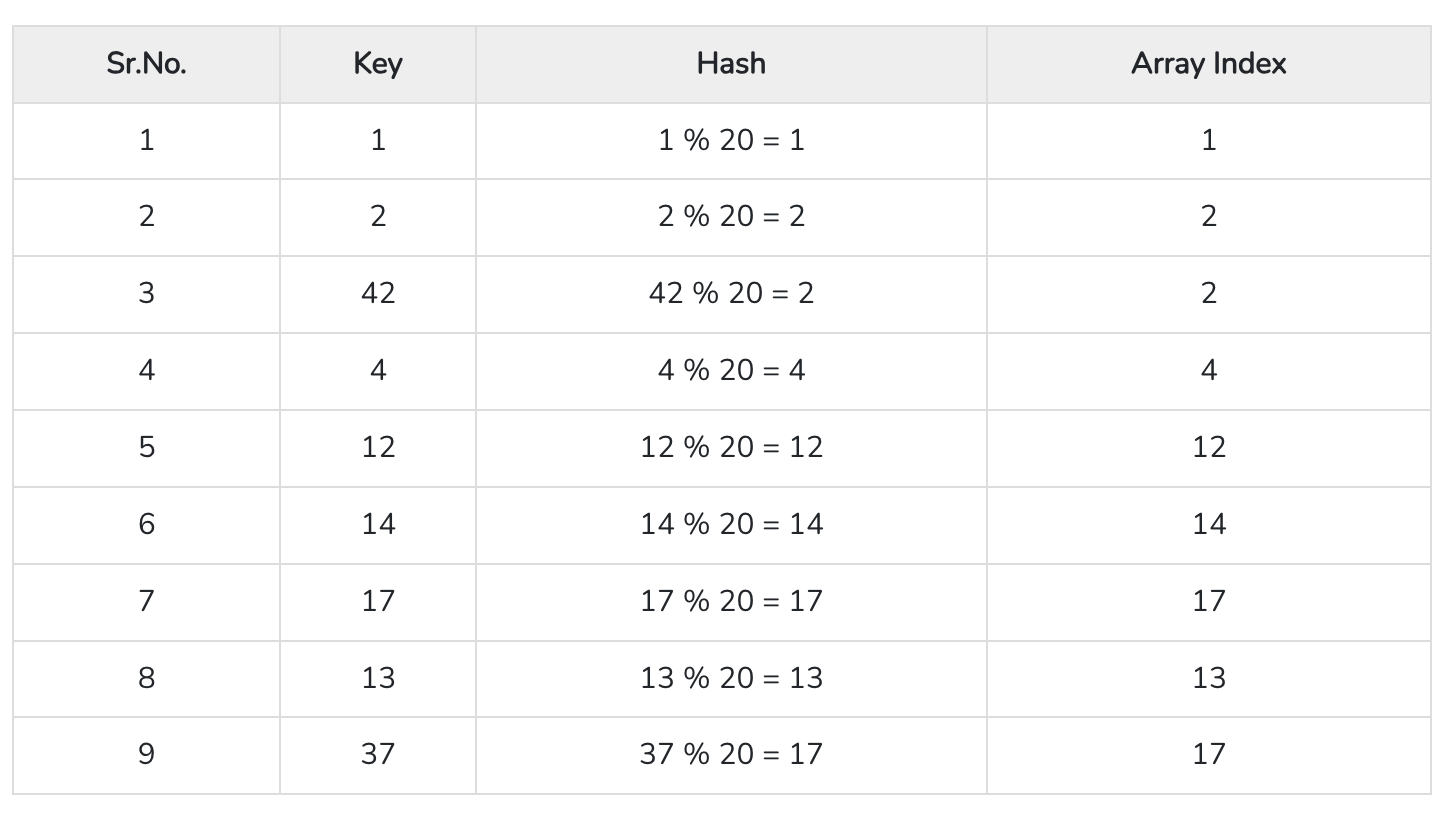
What happens when hash table resizes?
When a hash table resizes (grows), entries don’t stay where they were. The table allocates a new, larger backing array, then re-inserts (“rehashes”) every existing entry into the new array.