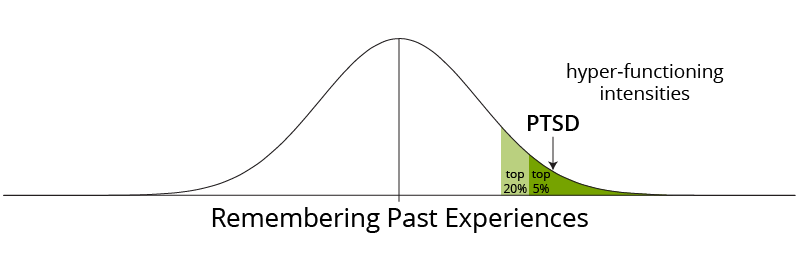
Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder (PTSD)
Like OCD, classification of Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder (PTSD) changed in DSM V. Again, although anxiety is a prominent symptom in PTSD, the condition’s etiology, treatment, and prognosis differs dramatically from other anxiety disorders. Currently, PTSD is included under a new syndrome category called Trauma- and Stressor-Related Disorders.
As its name suggests, PTSD is elicited following an experience with a traumatic event. This could be the result of a direct experience, such as engaging in military combat, or it could be the result of witnessing a traumatic event such as a fatal car accident. It could even be the result of witnessing the aftermath of a traumatic event such as a natural disaster.
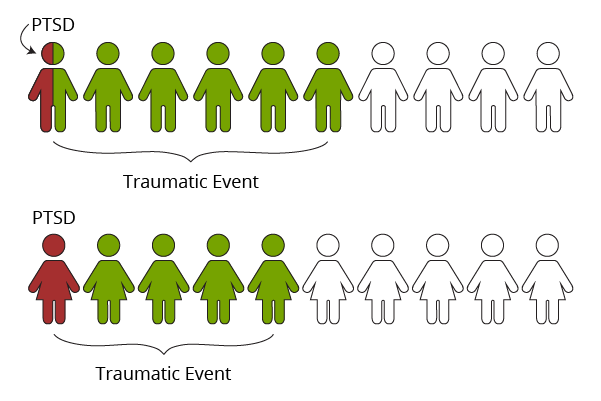
Whereas it is estimated that 60% of men and 50% of women experience a significantly traumatic event, the lifetime prevalence of PTSD is approximately 5% for men and 10% for women.
The parallel with OCD is that PTSD is the same thing but looking at the past.
OCD produces anxiety looking at the future. PTSD produces anxiety from looking at the past.
OCD
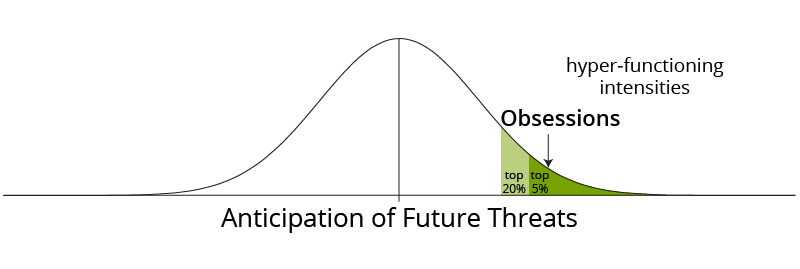
PTSD