Cell
 The mitochondria is the powerhouse of the cell LOL. That’s all I remember.
The mitochondria is the powerhouse of the cell LOL. That’s all I remember.
The cell is the simplest collection of matter than can be alive. Many single-celled organisms exist in nature.
• Most Organelles not visible with LIGHT MICROSCOPES – Organelles: membrane-enclosed structures within eukaryotic cells • 1950s – Electron microscope (EM) focuses beam of electrons through a specimen or onto its surface – EM can resolve structures about 2 nm across
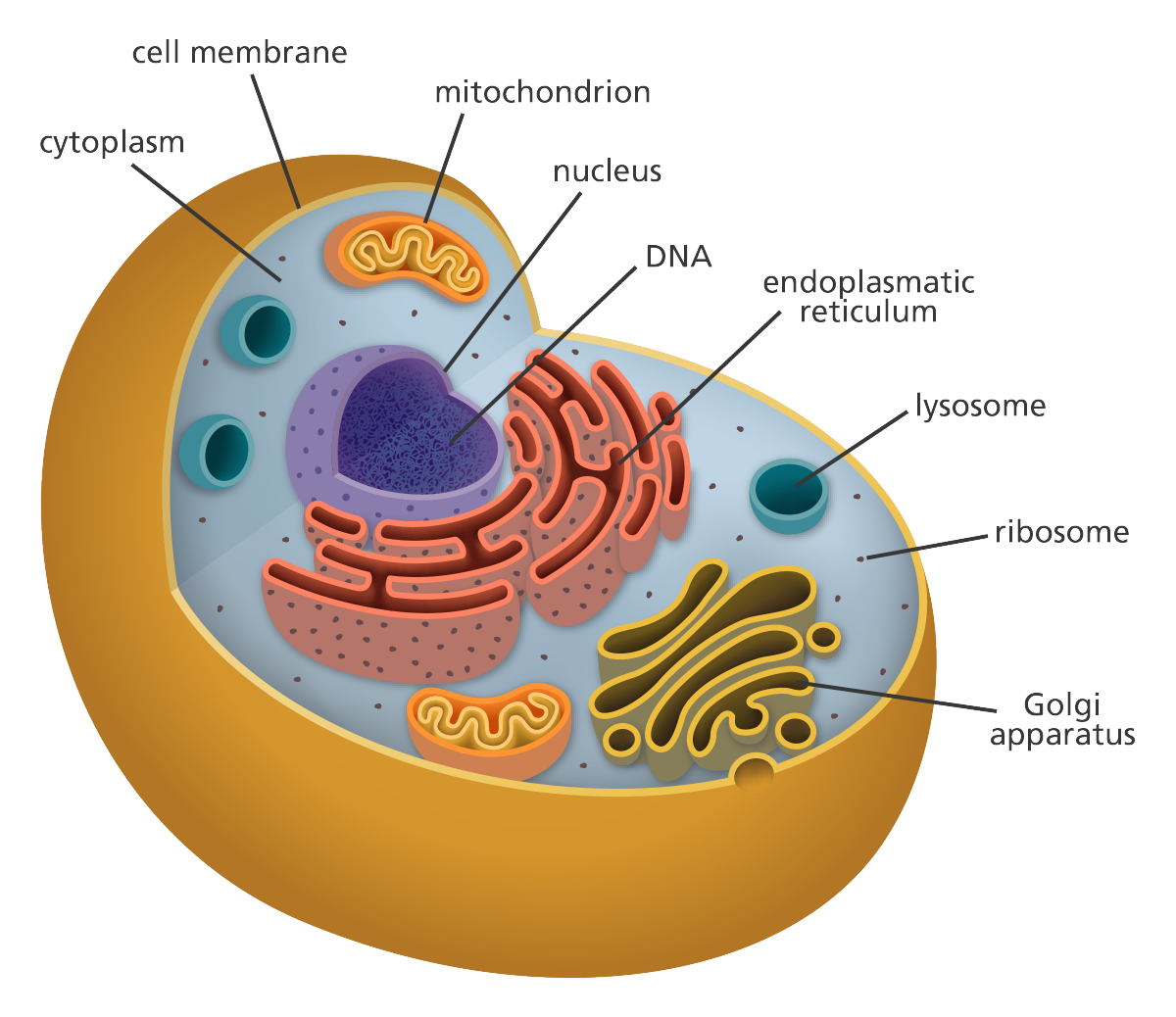
• ALL CELLS – Membrane-bounded by selective barrier called PLASMA MEMBRANE → Allows passage of oxygen, nutrients, waste for entire cell – Inside is semi-fluid cytosol (the aqueous component of the cytoplasm of a cell, within which various organelles and particles are suspended.) – Contain chromosomes which carry genes in form of DNA – Have ribosomes which make proteins
Prokaryotic Cell vs. Prokaryotic Cell vs. Eukaryotic Cell • Differ in the location of DNA – Most DNA in eukaryotic cells is in nucleus which is bounded by a double membrane – Prokaryotes: DNA in nucleoid (an irregularly shaped region within the cell of a prokaryote that contains all or most of the genetic material, called genophore. In contrast to the nucleus of a eukaryotic cell, it is not surrounded by a nuclear membrane) region (not membrane-enclosed)
| Prokaryotic Cell | Eukaryotic Cell | | :--- | :--- | | Bacteria & Archaea | Protists, fungi, animals, plants | | Have cell membrane, ribosomes, DNA, cytoplasm | Have cell membrane, ribosomes, DNA, cytoplasm | No Organelle | Have Organelle | DNA in nucleoid region | DNA housed in nucleus
• Interior is the CYTOPLASM – Cell bounded by plasma membrane – Eukaryotic cells: cytoplasm EXCLUDES the nucleus • Eukaryotic cells have a variety of ORGANELLES, which are → Suspended in cytosol in the cytoplasm → Membrane-bounded structures • Prokaryotic cells DO NOT have organelles
• RATIO OF SURFACE AREA TO VOLUME IS IMPORTANT – Limited amount of a substance can cross/second/area of membrane • As size INCREASES – Volume grows PROPORTIONATELY MORE than surface area
A smaller object has a GREATER RATIO OF SURFACE AREA TO VOLUME (area:volume) – Why most cells are small • Cells exchanging lots of material with surroundings may have projections – More surface area without adding much volume – MICROVILLI (microscopic cellular membrane protrusions that effectively increase the surface area of the cell and are useful for absorption and secretion functions) on intestinal cells
Eukaryotic cell organelles • 2 components involved in controlling genetics
- NUCLEUS → Contains most genetic info
- RIBOSOMES → Make proteins based on instructions from DNA