Conductor
Conductors: Materials that have a large number of electrons that are free to move when influenced by an E-field
- An ideal conductor has an unlimited supply of free charges
- Metals are close to perfect
Note
Conductors have loosely bound electrons (Valence Electron). As the conductor atoms come together to form a solid, these electrons can be highly mobile and are able to quickly move through the metal in response to electrical forces.
Properties of Conductors in E-Fields
- The electric field (external + induced) is zero inside a conductor
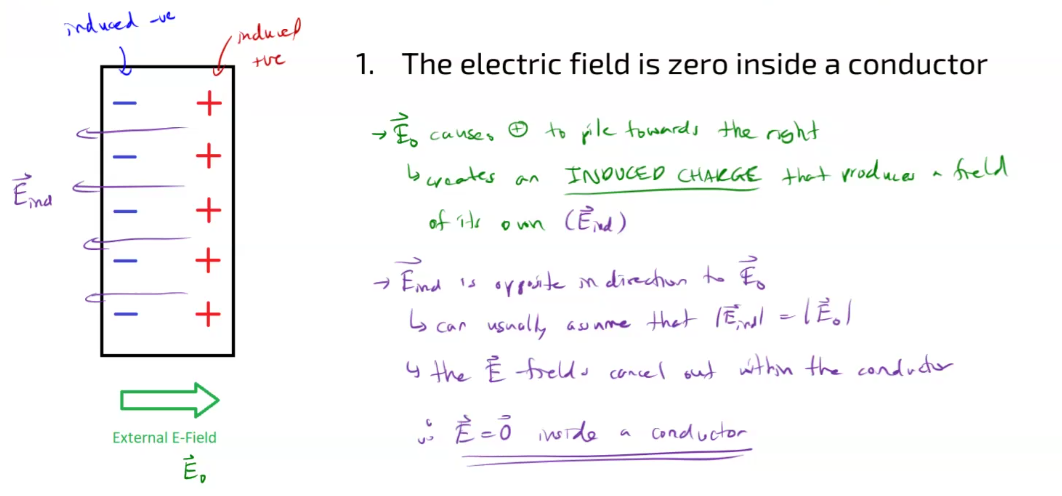
- The charge density is zero inside a conductor
- If inside a conductor, we can use Gauss Law so
- Electric Field inside conductor is 0 (includes cavities)
- Any net (excess) charge resides on the surface
- A conductor is an equipotential
- Since E = 0
- Electric field is perpendicular to the surface just outside a conductor
- Placing a charge inside a cavity
Faraday’s Cage: The electric field inside a cavity of a conductor is 0
Aha moments
This is related to ECE140. If electric field is 0, how do circuits work? Battery always create voltage. Voltage is related to electric field. aahh
Charge density relationships with Charge and radius and potential. https://uwaterloo.webex.com/recordingservice/sites/uwaterloo/recording/5ff1a43c6ccd103a9f6b00505681e6c2/playback