File Organization
Four ways introduced in SE350 to organize each file:
- Pile
- Sequential File
- Indexed Sequential File
- Indexed File
Warning
This is not about how to organize multiple files together, but rather how data is organized within a given file. How are groups of files managed? That is talked about in File Allocation.
Pile
- Data are collected in the order they arrive
- Purpose is to accumulate a mass of data and save it
- Records may have different fields
- No structure
- Record access is by exhaustive search
- Useful when data is only collected and stored prior to processing
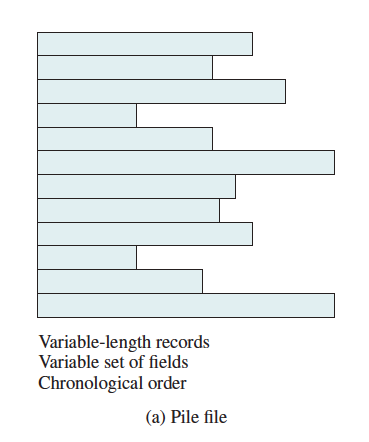
Sequential File
- Fixed format used for records
- Records are the same length
- All fields the same (order and length)
- Field names and lengths are attributes of the file
- One field is the key file
- Uniquely identifies the record
- Records are stored in key sequence
- Search is inefficient (look through the whole file)
- Updates are a pain, because physical organization matches the logical organization
- Overflow pile, transaction log & periodic batch updates to the file that rearranges the file
- Or: different physical layout from logical layout
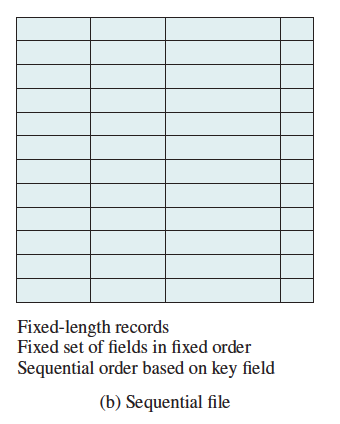
Indexed Sequential File
- Index provides a lookup capability to quickly reach the vicinity of the desired record
- Contains key field and a pointer to the main file
- Indexed is searched to find highest key value that is equal to or precedes the desired key value
- Search continues in the main file at the location indicated by the pointer
- New records are added to an overflow file
- Record in main file that precedes it is updated to contain a pointer to the new record
- Upon NULL pointer, continue in the main file
- The overflow is merged with the main file during a batch update
- Multiple levels of indexes for the same key field can be set up to increase efficiency
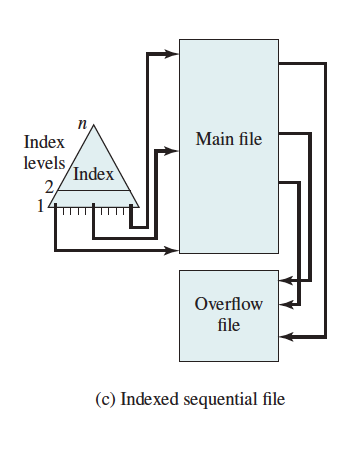
Indexed File
- Uses multiple indexes for different key fields
- May contain an exhaustive index that contains one entry for every record in the main file
- May contain a partial index