Filesystem
- Disk File Systems:
- NTFS: Widely used in Windows environments.
- FAT32, (OLD)
- exFAT: Designed for flash drives
- ext3/ext4: Used in Linux
- HFS+ (OLD apple FS)
- APFS: Apple File System
- Network File Systems: NFS, SMB/CIFS.
- Distributed File Systems: HDFS, Ceph.
- Flash File Systems: YAFFS, F2FS.
- Special-Purpose File Systems: procfs, sysfs, tmpfs.
Also IPFS for web3 lol
SE350
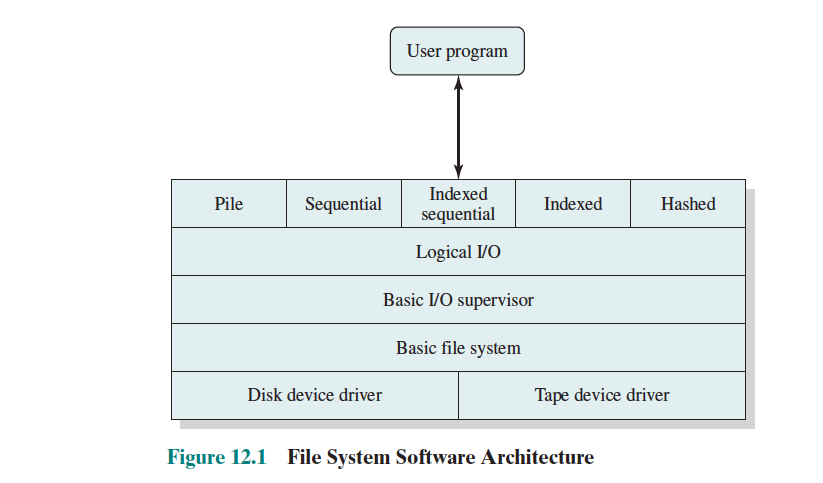
Why do we need filesystems?
- Long-term storage
- Sharable data between processes
- Structured, hierarchic relationships among files
Some terminology:
Field
- Basic element of data
- Contains a single value (student name)
- Characterized by its length and data type
Record
- Collection of related fields
- Treated as a unit
File
- Collection of similar records
- Treated as a single entity
- Have file names
- May restrict access
Database
- Collection of related data
- Relationships exist among elements
Typical File Operations
- Create
- Delete
- Open
- Close
- Read
- Write
- (Seek)
Typical Record Operations
- Retrieve All
- Retrieve One
- Retrieve Next
- Retrieve Previous
- Insert One
- Delete One
- Update One
- Retrieve Few
Records vs. Blocks
Records are the logical unit of access of a structured file, whereas blocks are the unit of I/O with secondary storage.
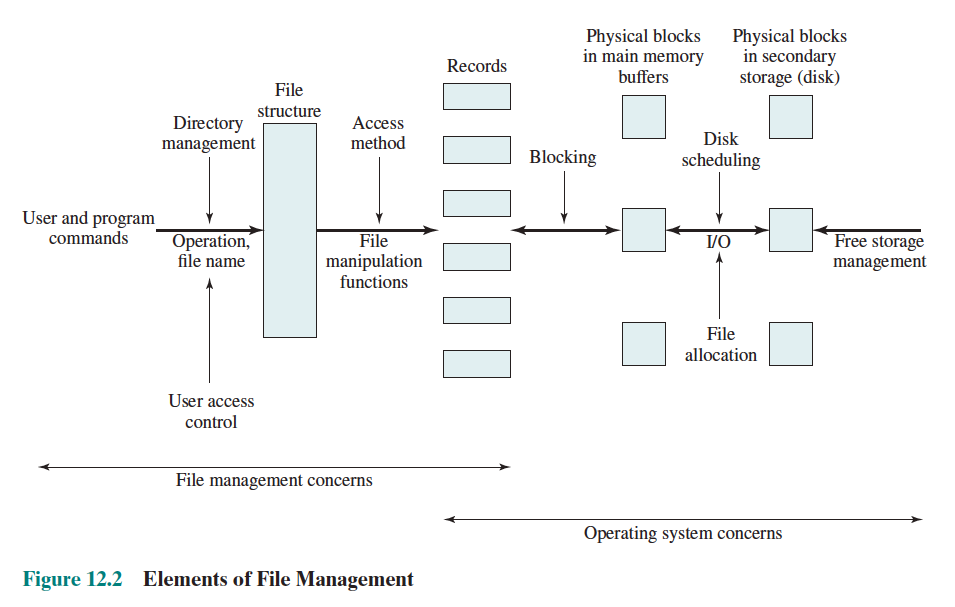
Concepts