Scheduler (OS)
The Scheduler is a component of the OS that decides which process runs at a given time. It selects processes from the queue based on certain criteria (scheduling algorithms).
Why is this concept important?
At a personal level, at NVIDIA, I realized that how we determine priority when things are competing for resources is determined through the scheduler.
Scheduling is the action of assigning resources to perform tasks.
- Resources: be processors, network links or expansion cards
- Tasks: be threads, processes or data flows
Resources
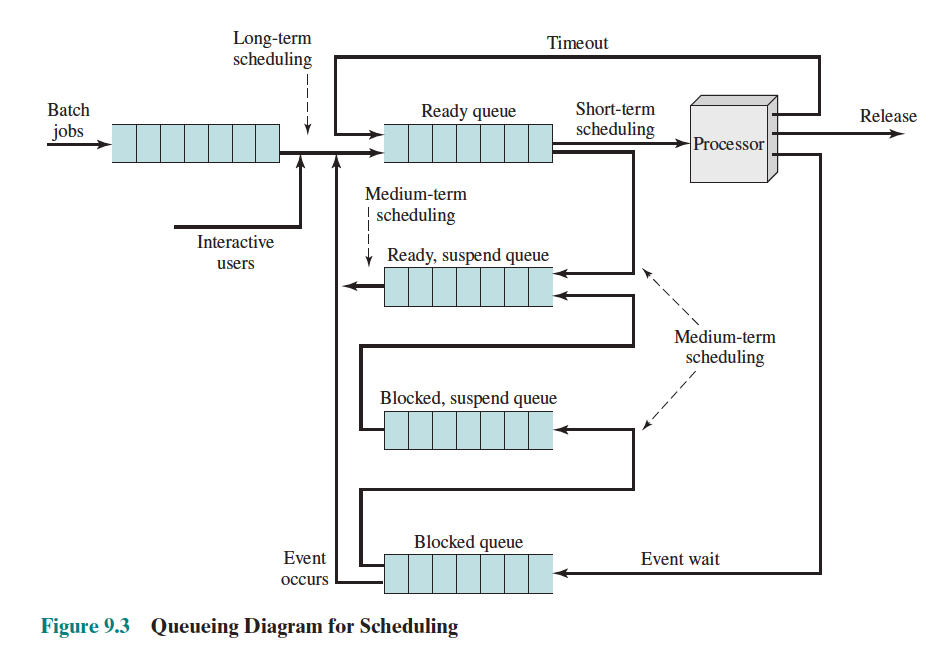
Levels of Schedulers
There is actually 3 different Levels of Schedulers:
- Short-Term Scheduling (decides which process to execute next)
- Medium-Term Scheduling (moving processes from secondary to main memory)
- Long-Term Scheduling (adding to the pool of processes to be executed)
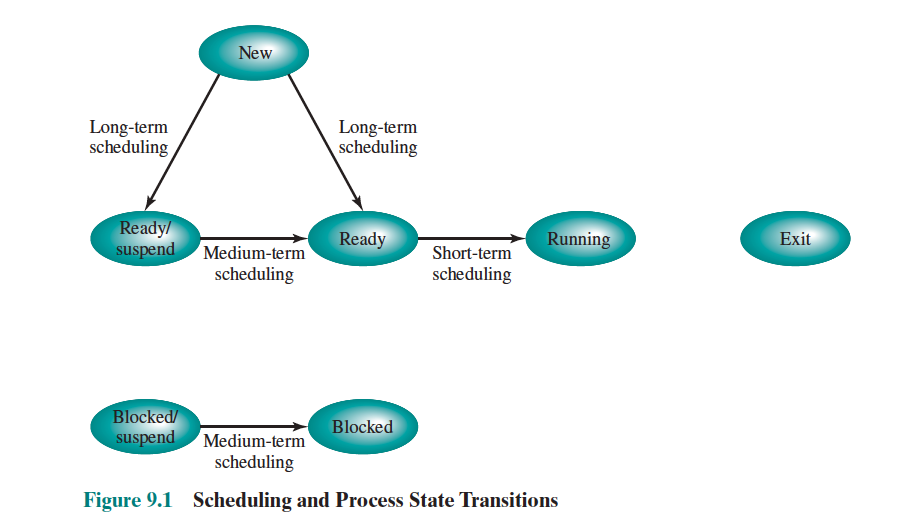
- Review your 5-State Process Model
Uniprocessor Scheduling
We start with uniprocessor schedulers, and then generalize to multiprocessor scheduling policies.
The types of scheduling policies introduced:
- First-Come-First-Served Scheduling (FCFS)
- Round Robin modern ones based on clocks
- Shortest Process Next (SPN)
- Shortest Remaining Time (SRT)
- Highest Response Ratio Next (HRRN)
- Feedback-Based Scheduling
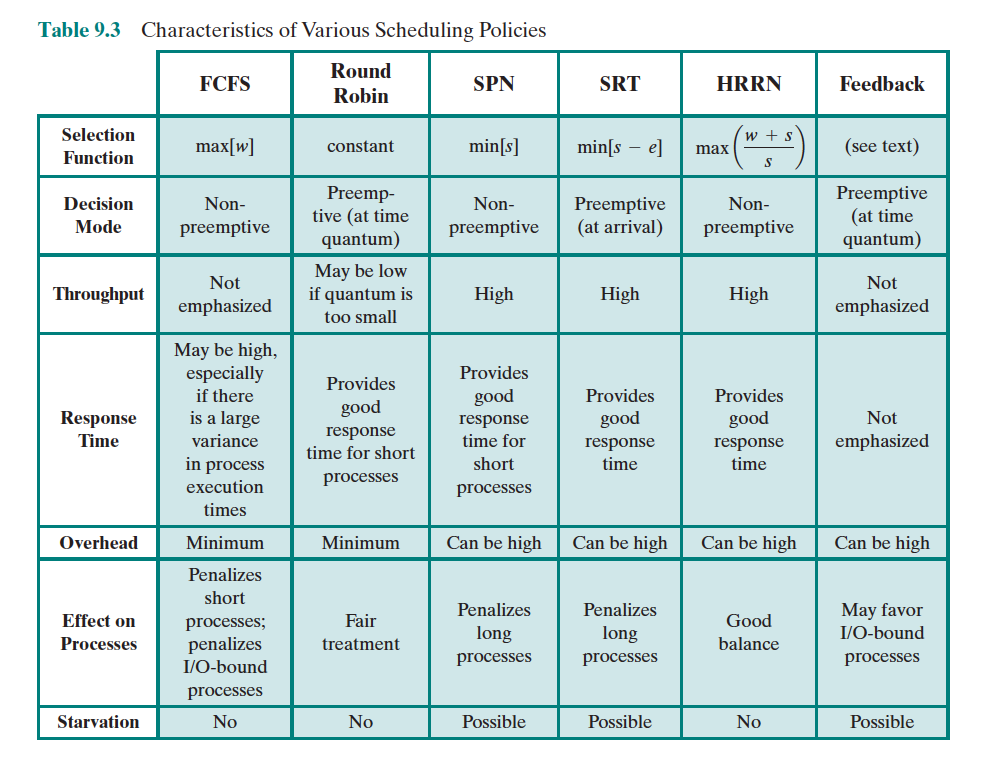
- w = time spent in system so far, waiting
- e = time spent in execution so far
- s = total service time required by the process, including e; generally, this quantity must be estimated or supplied by the user
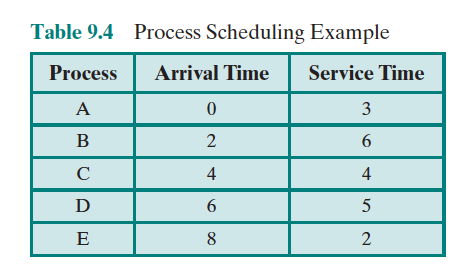
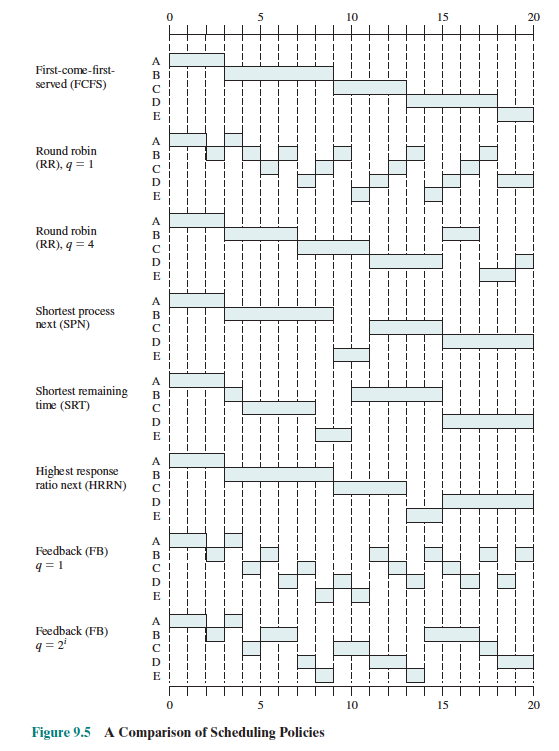
Below is how different schedulers would work based on the following process requirements:
Other concepts:
- Fair-Share Scheduler
- Multi-Level Feedback Queue → this is actually what is used in real-life