Thread
Also see thread (C++) for software usage.
A thread is a unit of execution with a Process.
- a thread is a lightweight execution unit (source from ROS2 tutorial)
Resources
Within a process, each thread has:
- A thread execution state (Running, Ready, etc.)
- A saved thread context when not running;
- An execution stack
- Some per-thread static storage for local variables
- Access to the memory and resources of its process (shared amongst threads)
One way to think about it
You can see a thread as an independent program counter operating within a process.
The advantages of threads over processes...
- Less time to create a new thread than a process (~10x faster)
- Less time to terminate a thread than a process
- Less time to switch between two threads within the same process
- Threads enhance efficiency in communication between different executing programs
- because threads within the same process share memory and files so don’t have to invoke the kernel
But why is thread switching faster?
See Thread Switch.
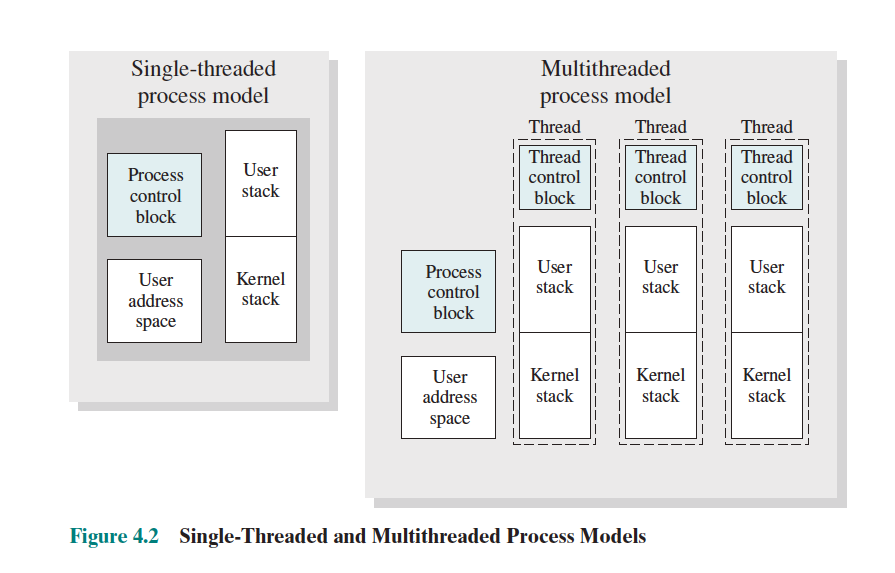
- You can see that they all share the same PCB and address space, but now each thread have their own user stack and kernel stack
There are 2 kinds threads:
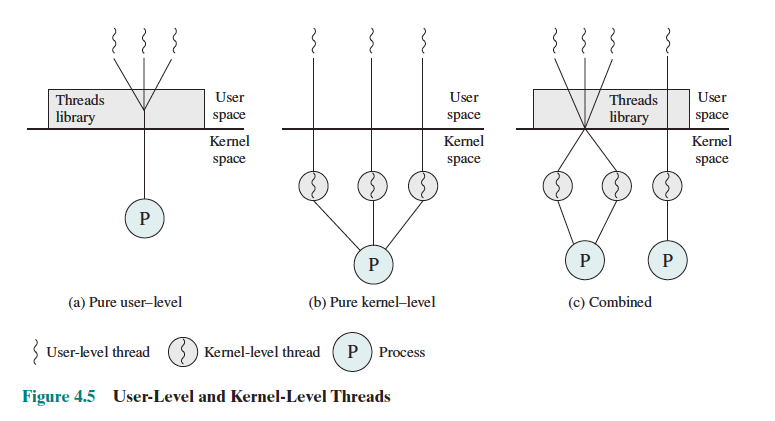
In a multicore system, how do the threads run? See Multiprocessor Scheduling.
Other Concepts