Legendary book Also see Telecommunications, Telecommunications, 5G, Telecommunications, 5G, 5G, Computer Network
Cellular Network
Quite different from the Wifi.
Seamless transition from LTE to NR. This is so cool.
Mobile Telephony Evolution
1st Generation (1G) - Analogue Speech 2nd Generation (2G) - Digital Speech + medium-rate data 3rd Generation (3G) - High Speed data, multiple services, quality 1st Generation (4G Mobile Core) (LTE) - Higher speed data, PS Only, multiple services, quality 5G NR- Ultra High Speed data, low latency, new use cases (IoT)
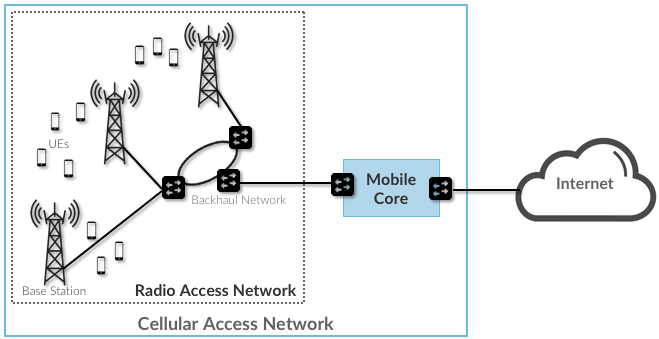
The cellular network provides wireless connectivity to moving devices (called UE).
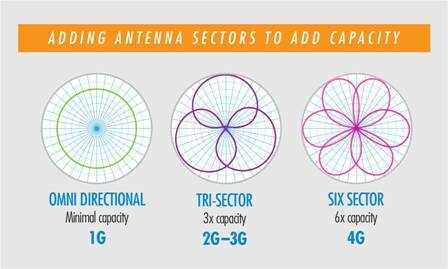
The Cell (in a hexagonal shape)
- Basic Unit of the cellular Network
- Radio coverage of one base station
- Types of Cells:
- Omnidirectional cell
- Sectorized cell
The UE can move between one cell between the other, and this is what you are learning Steven, how to handle that.
Anatomy
Note: This seems different from what I have learned, because of the terminology.
UE → Access Network (RAN) → Core Network (Mobile Core) → External Networks
Access Network: Providing users with wireless access to the core network
- Radio Access Network
- Mobile Access Network (there is a difference!) Core Network: Core center of the network.
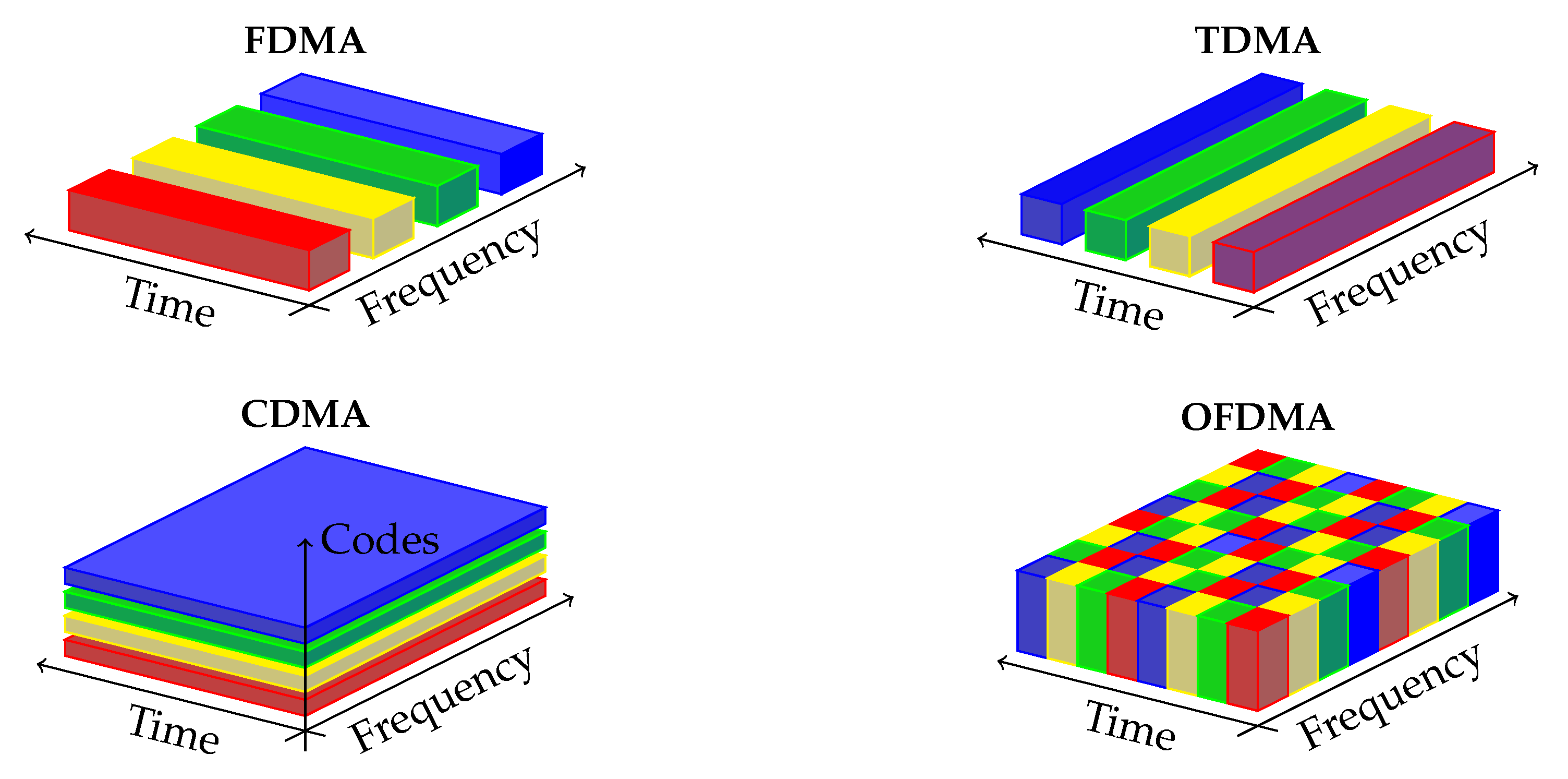
Access Techniques
Frequency Division Multiple Access (FDMA)
- Each user has their own frequency slot
- All users transfer at the same time
Time Division Multiple Access (TDMA)
- Each user has one time slot
- Frequency domain is shared, users are separated in time
Code Division Multiple Access (CDMA)
- Users share same frequency and time
- Users (channels) are separated out using unique codes
Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiple Access (OFDMA)
- Each user and each channel has unique time and frequency resource
- Many users are separated in frequency and/or time
Resource Sharing
How do hosts share a network?
Concept of multiplexing: a system resource is shared among multiple users.
Synchronous time-division multiplexing (STDM): divide time into equal-sized quanta and, in a round-robin fashion, give each flow a chance to send its data over the physical link.
Frequency-division multiplexing (FDM): is to transmit each flow over the physical link at a different frequency, much the same way that the signals for different TV stations are transmitted at a different frequency over the airwaves or on a coaxial cable TV link.
Simplified 2G Architecture
For Circuit Switched
Base Transceiver Station (BTS):
- Wireless connectivity with UE
Base Station Controller (BSC):
- Access control
- Connection control
- Mobility control
- Radio Resource Manamgenet
Mobile Switching Center (MSC):
- Register UEs
- Connection Control
- Tracking of UEs
- Mobility Control
- Call Session Control
- Circuit Switched Data Transfer
Gateway MSC Server (GMSC Server)
- Routing calls to mobile subscribers
- Interface with external networks Home Location (HLR):
- Subscriber database
- Access, mobility and security information
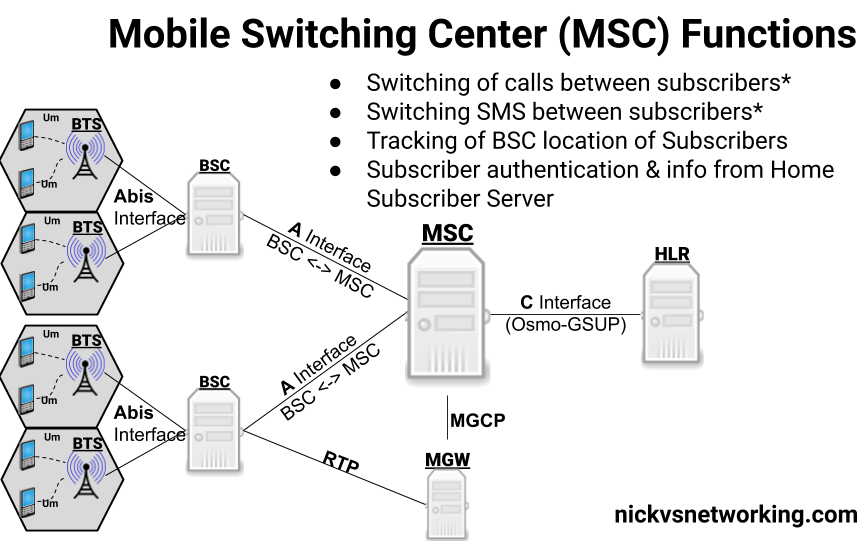
For Packet Switched
Serving GPRS Support Node (SGSN):
- Register UEs
- Connection Control
- Tracking of UEs
- Mobility Control
- Data session control
- Data Transfer
Gateway GPRS Support Node (GGSN)
- Data Transfer
- Bridge to external networks
- Output of charging data
IP Multimedia SubsystemIMS
Security and Mobility (TODO)
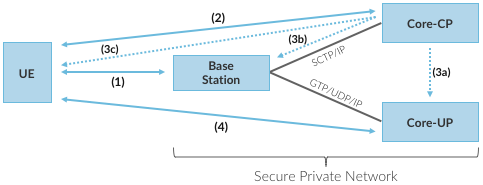
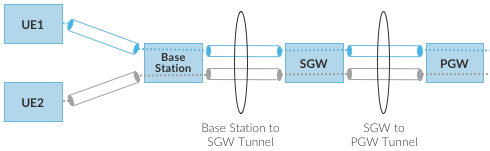
Sequence of per-hop tunnels involved in an end-to-end User Plane channel