Dynamic Array
Arrays have a fixed size. Vectors / Dynamic Arrays can change in sizes. In C++, the vector library exists for a variable size array, but not in C.
C++ Vector
vector<int> v;
v.push_back(5);
v.push_back(2);
cout << v.back() << "\n"; // 2
v.pop_back();
cout << v.back() << "\n"; // 5The following code creates a vector with five elements:
vector<int> v = {2,4,2,5,1};Another way to create a vector is to give the number of elements and the initial value for each element:
vector<int> v (10); // size 10, initial value 0
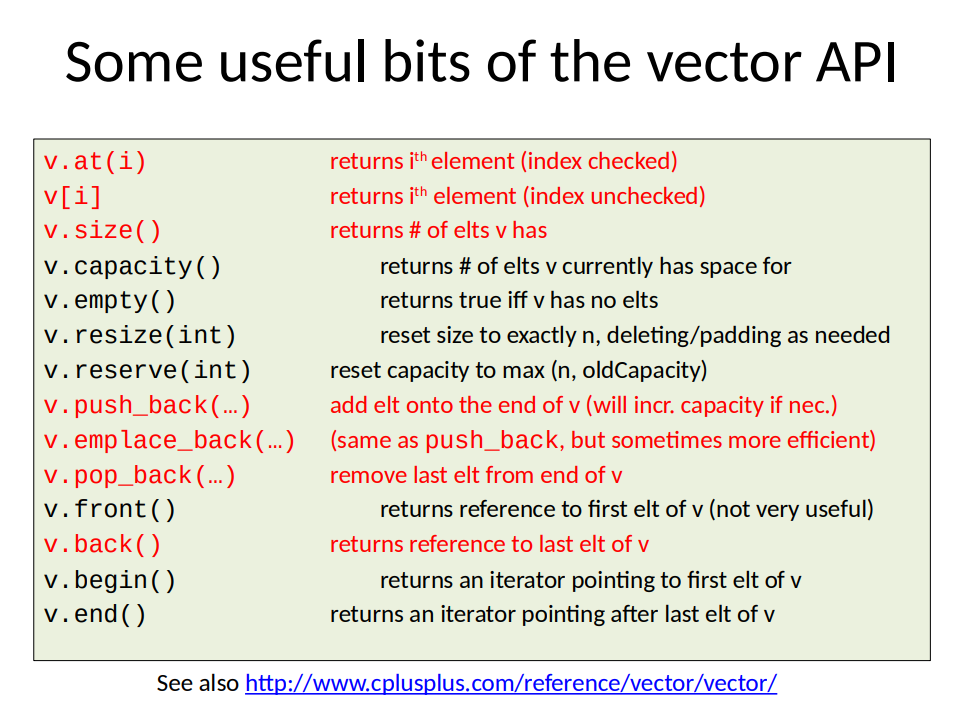
vector<int> v (10, 5); // size 10, initial value 5Other Useful vector APIs
Dynamic Array
Dynamic arrays are arrays allocated on the heap.
int* arr = new int[length]; // (content is garbage) (length can be a runtime variable)
int* arr = new int[length] {}; // initialize content to 0Content of freshly allocated array is garbage unless initialized with () or {} that default to 0.
To free dynamic array:
delete[] arr;Difference with static array (ex: int arr[10])
- Static arrays are allocated on the stack.
- Static arrays size must be fixed (compile time constant).
Time Complexity of Dynamic Arrays#card
- Indexing:
- Search:
- Insertion:
- Deletion:
- Optimized Search:
2D Array
vector<vector<int>> vec(n, vector<int> (m, 0));If you want to specify the directions, you can do the following:
vector<vector<int>> directions = {
{0,1},
{0,-1},
{-1,0},
{1,0},
}Miscellaneous
emplace_back vs. push_back?
This is good nuance
Links:
- https://stackoverflow.com/questions/4303513/push-back-vs-emplace-back
- https://en.cppreference.com/w/cpp/container/vector/emplace_back
For emplace_back, constructor A (int x_arg) will be called.
For push_back, A (int x_arg) is called first and move A (A &&rhs) is called afterward.
std::vector<A> v;
v.push_back(A(x_arg));From above:
A(int)constructs a temporaryAfromx_argvector::push_back(T&&)moves that temporary into the vector usingA(A&&)(or copies if move isn’t viable)