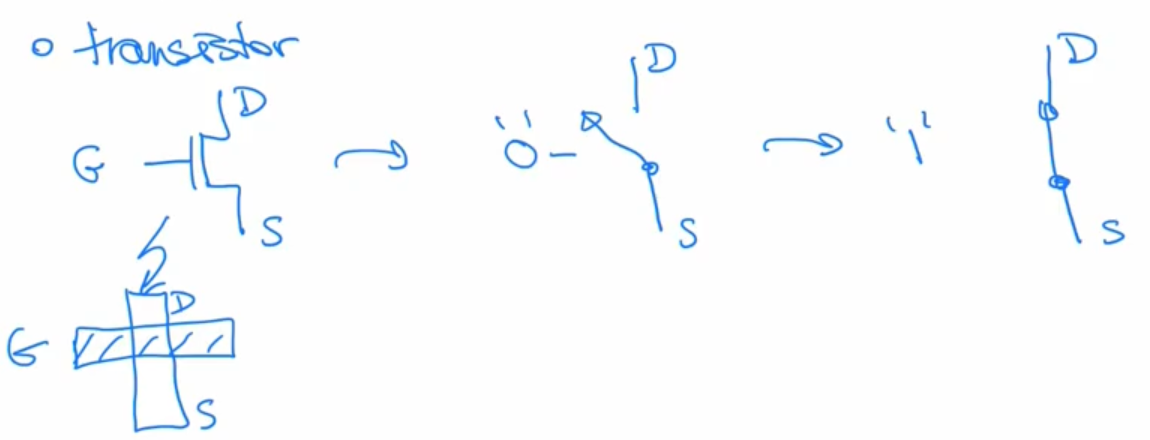
MOSFET
Stands for metal–oxide–Semiconductor field-effect transistor.
Has two major types:
- NMOS (N-channel MOSFET)
- PMOS (P-channel MOSFET)
| Feature | NMOS | PMOS |
|---|---|---|
| Type of charge carrier | Electrons (fast) | Holes (slow) |
| When does it turn ON? | When gate voltage is HIGH | When gate voltage is LOW |
| Speed | Faster | Slower |
| Common usage | Used for fast switching | Often used in combination with NMOS |
Has three terminals: Gate (G), Drain (D), Source (S).
A MOSFET transistor has
- A Drain
- A Source
- A Gate
The gate controls the flow from the source to the drain.
Transistors on CPU
Okay, so now, I understand how a single transistor can be powered. But I don’t see how we can power so many transistors, and all this intricate wiring to power billions of transistors in a SINGLE CPU?
Speaking of which, GPUs also run on transistors?
This is a really good video with really good visualization.
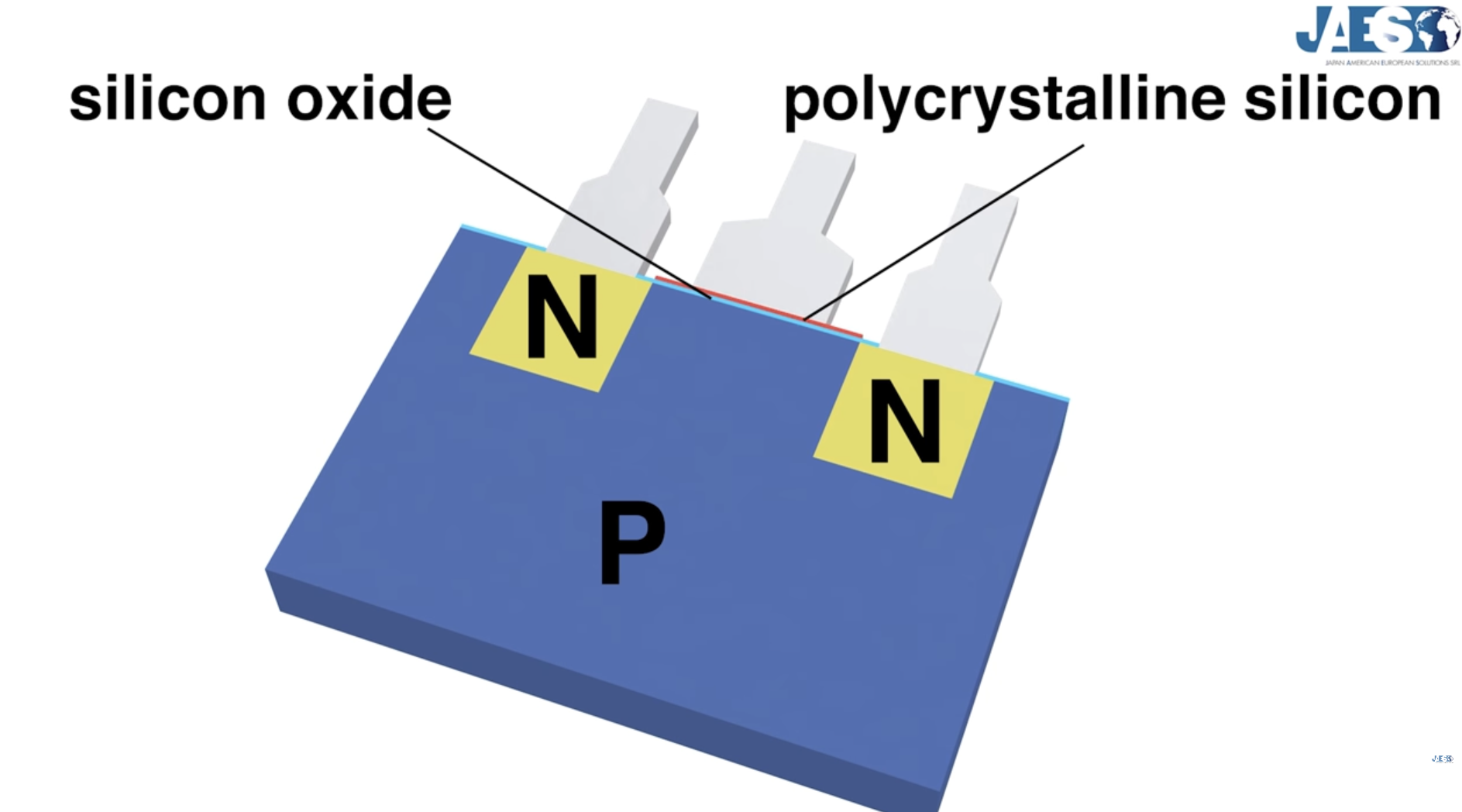
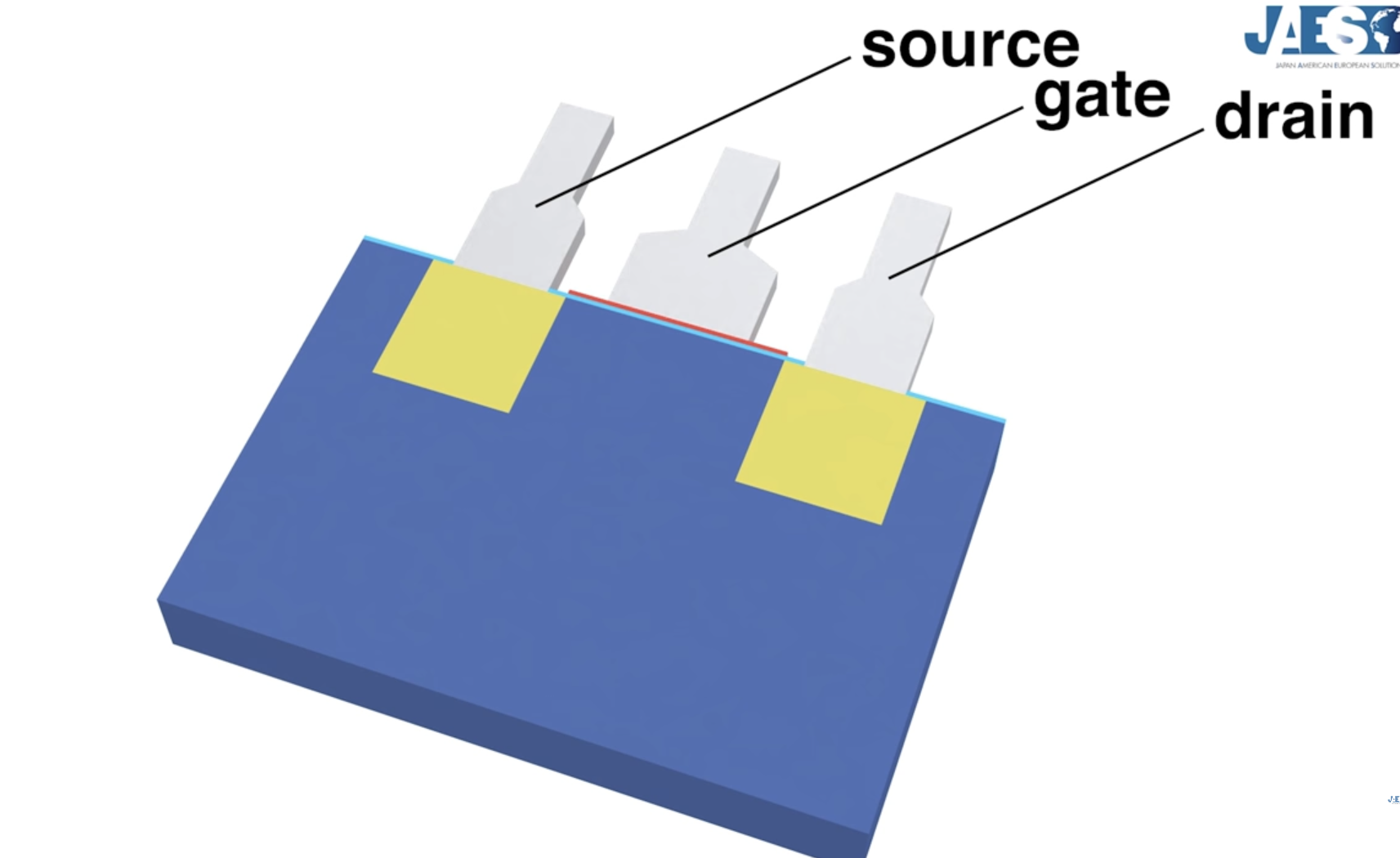
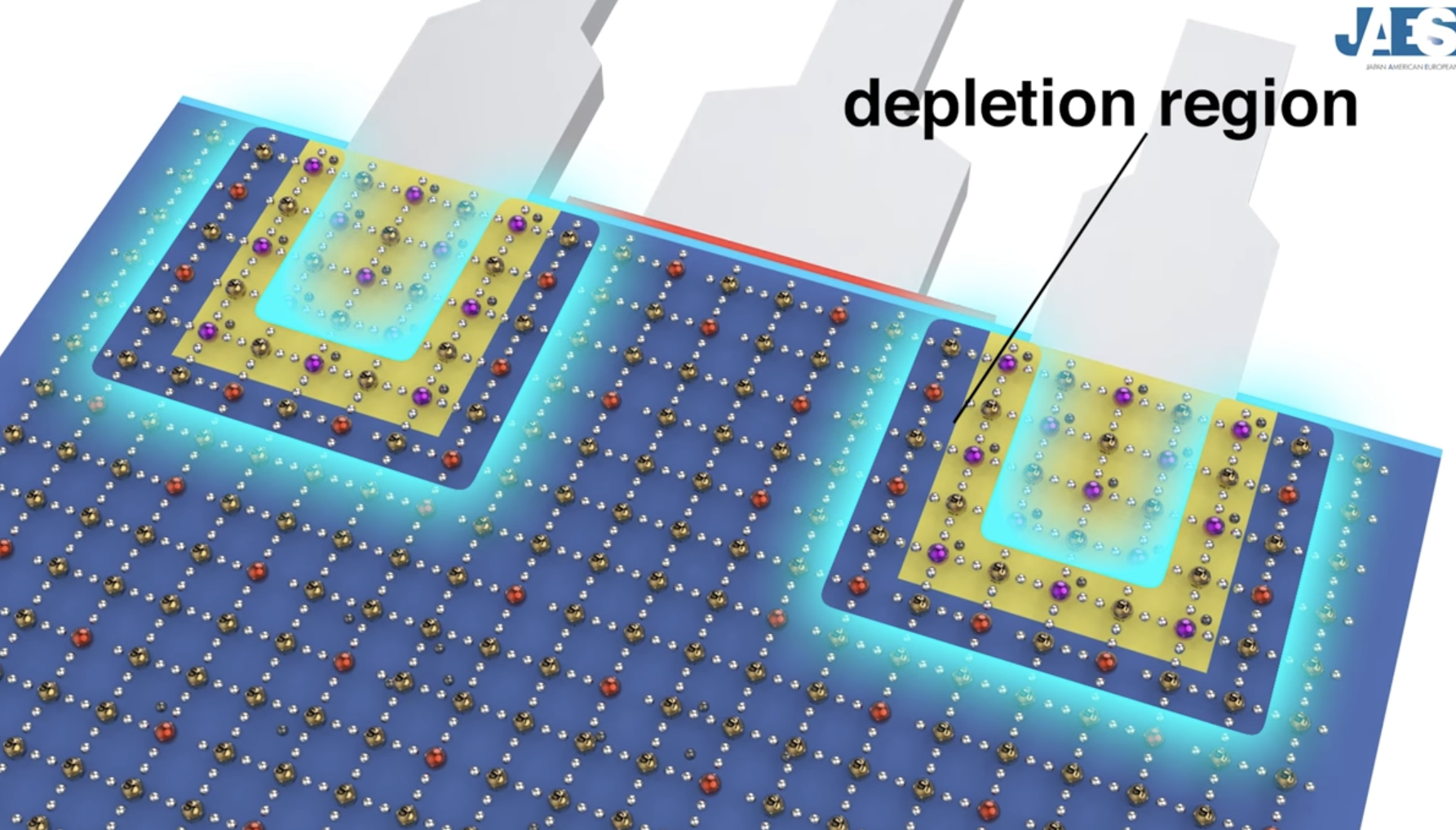
Linus Tech Tips also toured the Intel Fab, which is SUPER insightful
You should also watch Sam Zeloof videos to understand.