Transistor
I’ve always been intimidated by them, but essentially they are just a Logic Gate!
A transistor is an on/off switch controlled by an electric signal. Transistors the the building blocks of modern day computer circuits.
The transistor
The Integrated Circuit combines hundred of Transistors into a single chip.
Types of transistors:
- MOSFET Transistor (voltage controlled)
- Used to design CPUs and GPUs, also SRAM and DRAM
- BJT Transistor (Current controlled)
- Used in RF
- Ben Eater explained it through here
Why MOSFET and not BJT?
- Higher power consumption: Compared to CMOS transistors, BJTs consume more power because they rely on continuous base current.
- Slower switching speeds: MOSFETs and FinFETs have much lower gate capacitance, allowing for faster operation in digital circuits.
- Lower integration density: BJTs are harder to miniaturize, making them unsuitable for modern high-density ICs.
Electronic component that behave in a non-linear/discrete manner. Transistors are combined to form circuits, they are the basis of Logic Gate.
Types of Transistor
Ethan Childerhorse taught me this, but there are two types of transistors really.
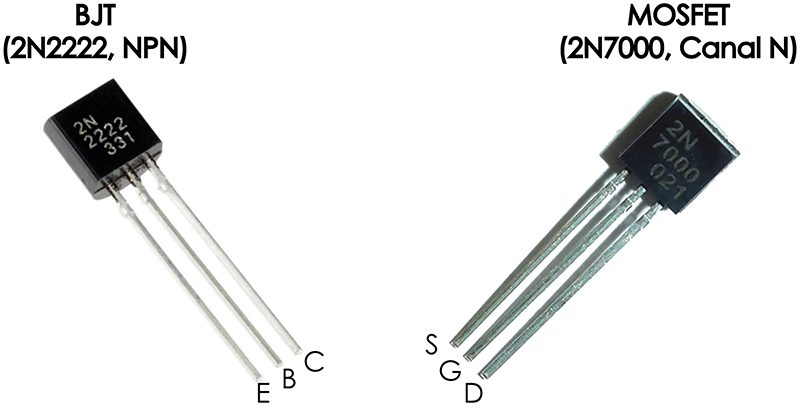
Thoughts
So logic gates are made from transistors.
These transistors are all powered by some source (like battery). But who controls how these transistors on and off. Is it a chain reaction?
These are actually how the gates are implemented with transistors http://hyperphysics.phy-astr.gsu.edu/hbase/Electronic/trangate.html
So logic gates/transistors combine control inputs. Where do these control inputs come from?
- In the simplest case, think if you want to use a flip-flop to store data. You input the data you want to store
- Now, go up a level of abstraction. You write a program that stores the data that you entered from your keyboard. The IO sends data to a microcontroller
Then the question is like, how does a microcontroller work?
Old Notes
Transistors Explained by Engineering Mindset Transistors come in different shapes and sizes.
BIpolar and Field effect.
Small electronic compoennts with two main functions,
- switch circuits on and off
- Amplify signals
Three pins,
Emitter Base Collector
Why do we use transistors?
We can use a switch in a lightbulb and battery circuit.
0.6V to 0.8V for transistor to turn on.
NPN transitor
Conductor vs Insulator vs Semiconductor