Power Transmission
Source of knowledge: https://uwaterloo.atlassian.net/wiki/spaces/EIC/pages/31727390687/Power+Transmission
Power transmission refers to a transfer of energy from a power source to another device. These systems provide speed, torque, and/or direction of rotation conversion.
Why is this important?
This is SO IMPORTANT to master. Every time you apply force, you need to think about how power is being transferred. Think about how we transfer the power from an engine into the rotation of the wheels (we need a transmission system, the Drivetrain).
With Motors, there is always the tradeoff between Torque and RPM. See Horsepower.
In Practice
Apparently, the gears shouldn’t be pushing against each other too much? Like there should be a little plug between the gears? I saw from this video at 5:51. If you can fit a paper through, it’s good. Idk how good this is. Ahh, it’s called Backlash.
Power Transmission Components
Power Transmission Systems
Gear Drive
Gear drives are the most widespread form of mechanical transmission.
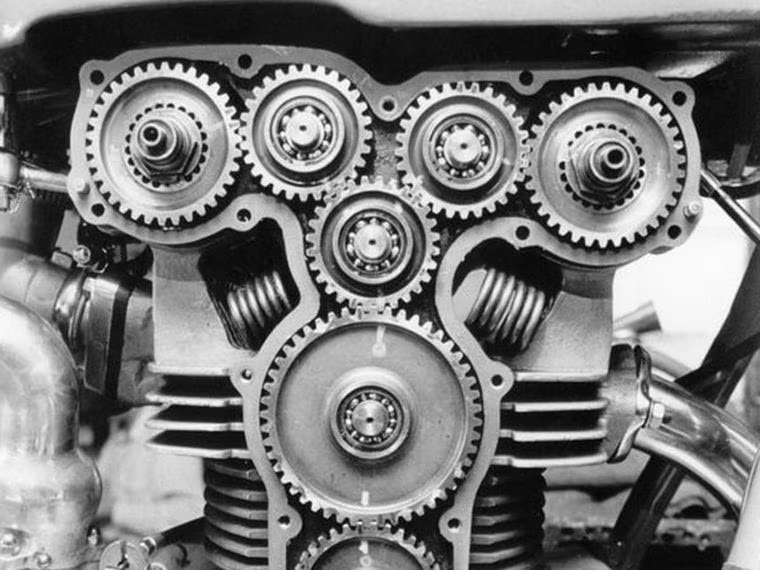
The main advantages of gear drives are:
- Compact structure (suitable for short range transmission)
- High efficiency (efficiency loss of 1-2 percent), lack of slippage
- High reliability and long life
The shortcomings of gear drives are
- Not suitable for transmission between two axes at a long distance. Furthermore, they require a high level of precision in manufacture and installation, resulting in higher costs. It should be noted that gear drives are incredibly versatile, as they can be found in, both, small scale and large scale applications.
Belt Drive
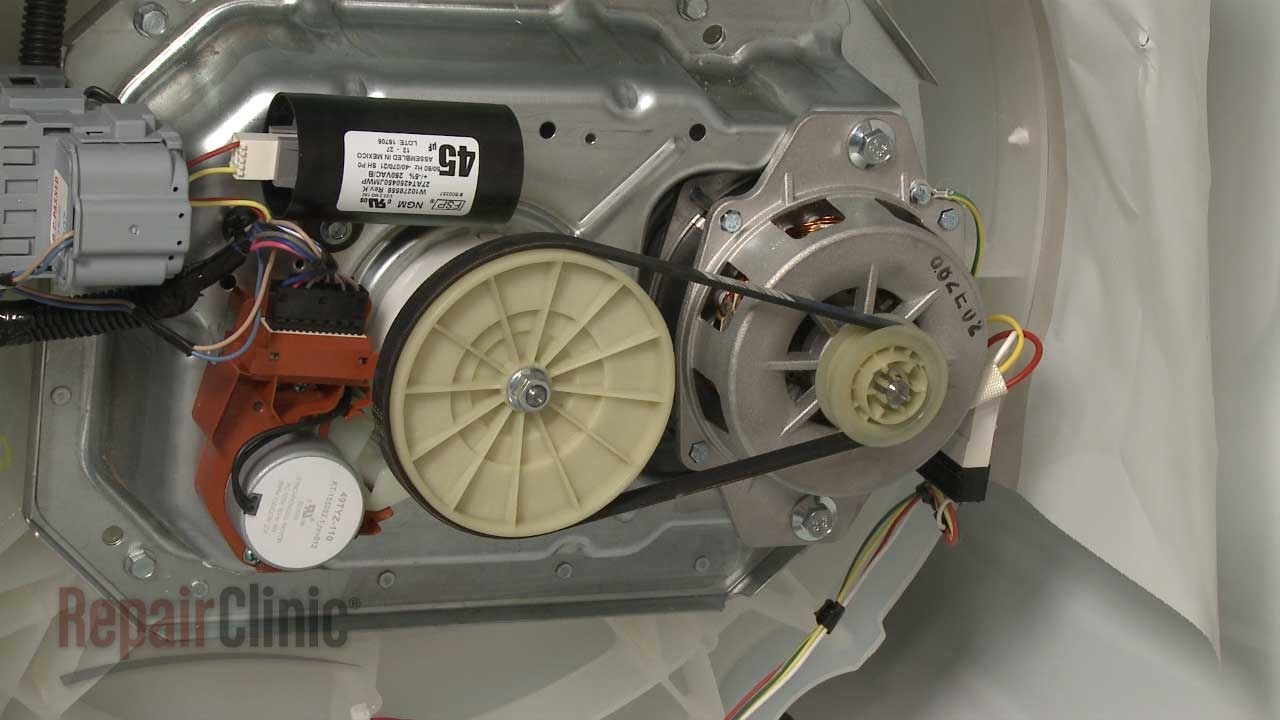 Belts are a simple, effective and cheap way of transmitting power but is a less efficient than other common power transmission devices.
Belts are a simple, effective and cheap way of transmitting power but is a less efficient than other common power transmission devices.
Advantages:
- Tolerance to impact and vibration which can help prevent damage. If there is an overload, the belt can slip off to avoid breaking the machine.
- Easy setup and tensioning
- have one of the pulleys on a slot or some tightening mechanism so it can pull the belt taut into position. In many custom use cases, using common sizes found on the market might not be taut without designing a potential inefficient route for the belt. Instead, using tensioning guide wheels can get a taut fit to taut transfer power.
Disadvantage:
- Since the belt is not perfectly fixed and can vary in tension and in slip conditions, it is not guaranteed to get a fixed gear ratio. This inaccuracy makes the belt drive more inefficient and the diameter ratio is often larger (than a gear drive), resulting in a larger outer dimension
- A relatively short service life compared to other transmission systems due to the wear and tear on the softer belt material
Common application of belt drives
- washing machines as well
- drill presses (many drill presses vary speed by opening up the drill press and moving the belt between different sizes of pulleys) cool!
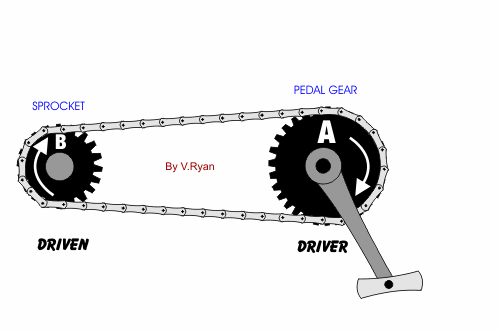
Chain Drive
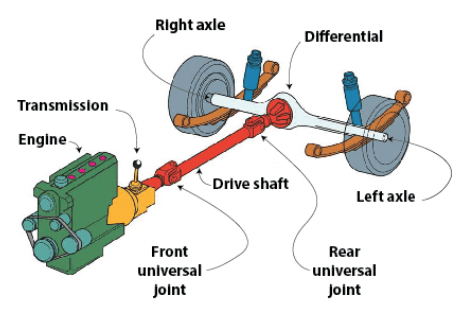
Shaft Drive
Shaft drives are most often used in vehicle Drivetrains. In a standard ICE (internal combustion engine) car, there is:
- a drive train that moves the car body
- This rear wheel drive train contains the engine, transmission, clutch, drive shaft, differential with drive axles (smaller drive shafts)
- The engine provides power which goes through a series of gearing in the transmission to change the output torque and speed. when the clutch is engaged. The output is then delivered through the drive shaft to the differential that sends proportional power to the rear wheels.
- Differential allows the rear tires to spin at different rates (hence the name differential) incase the tires are on different surfaces or experience different forces.
Old Notes
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=JOLtS4VUcvQ
Shifting gears but things are being spun does not work
Synchronizer is invented to make that happen, prevent clash
Automatic vs. Manual Transmission
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=auQgOtveQi0 Automatic transition is automatic transmission
manual transmission uses torque pad
We have the engine running constant RPM so it runs at optimal RPM,
Manual transmission has an intermediate shaft, Gear change results in speed drop.
Automatic transmission to overcome power drop in gear change. It uses a planetary gearset design. 2 inputs and 1 input.