Motor
Motors are powerful and amazing. Now that I took ECE106 and ECE140, I have a much better understanding to understand how motors work.
Videos
- How does an Electric Motor work? (DC Motor) (best video)
- Motor Basics (comprehensive)
- Types Of Electric Motors - DC | AC | Synchronous | Brushless | Brushed | Stepper | Servo - YouTube by Electronoobs
- Focus on AC motors: Ultimate Beginners Guide to Using Electric Motors for Makers and DIY Projects; #068 by Jeremy Fielding
- Motor Control 101
Articles
- https://www.nxp.com/docs/en/brochure/BBMTRCNTRLART.pdf
- https://www.elprocus.com/different-types-of-electric-motors/
See the Motor Category canvas for the high level tree.
Basics of Motors
Notes from
Motor
An electric motor is a device converting electrical energy into mechanical energy (generally a torque).
This conversion is usually obtained through the generation of a Magnetic Field by means of a Current flowing into one or more coils.
The specific relationship between current and magnetic field generated by a Solenoid is given by:

where (you learned from ECE106), see Magnetic Field
The maximum output torque, and then the maximum efficiency, is obtained when the load angle is 90°
- The rotation is obtained thanks to the attractive force between two magnetic fields:
- One field is located on the rotor (the moving part)
- The second magnetic field is located on the stator (the body of the motor)
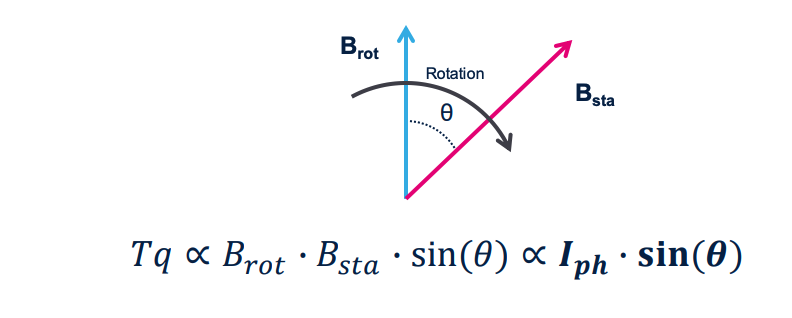
Usually
- One magnetic field is generated by a permanent magnet (stator)
- Other one is generated through an electromagnet (solenoid).
he rotation of the rotor magnetic field (Brot) causes a variation of the magnetic flux in the solenoid.
Consequently an electro-motive force facing the flux variation is generated (Lenz’s law). This effect is named back electro-motive force (aka BEMF) and it is proportional to the motor speed according to the formula:
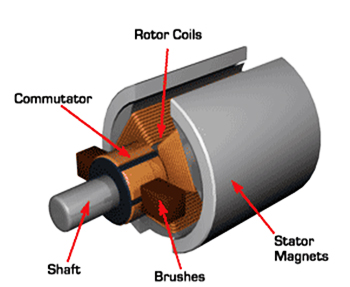
For example, look at this Brushed DC Motor:
Categories of motors
We can divide Motors divide in 2 main types
- Synchronous Motor
- Asynchronous Motor (Induction Motor)