Visual SLAM
Visual uses cameras to simultaneously localize and construct a map of the environment in real-time.
Tesla doesn’t seem to use visual SLAM. Instead, it does planning using an Occupancy Network.
I made a YouTube video where I built Visual SLAM from scratch, has some nice animations and I spent quite a bit of time on it. Do check it out :)
Resources
- SLAM Textbook (BEST textbook)
- Lecture: Photogrammetry I & II (2021, Uni Bonn, Cyrill Stachniss) (BEST lectures)
- I do find some of the lectures to be too technical, more information than needed, so useful if you want to go down abstraction
- https://www.kudan.io/blog/camera-basics-visual-slam/
- https://faculty.cc.gatech.edu/~afb/classes/CS7495-Fall2014/presentations/visual_slam.pdf
You basically try to figure out where the features align.
Visual SLAM Concepts
Visual SLAM Implementations
- ORB-SLAM (most popular)
- DROID-SLAM seems to be state-of-the-art https://github.com/princeton-vl/DROID-SLAM, deep learning-based SLAM, and trained end-to-end via pytorch
- https://github.com/openxrlab/xrslam
- This guy’s student implementation of SLAM might be good https://github.com/MiguelAngelCalveraUnizar/Mini-SLAM_student
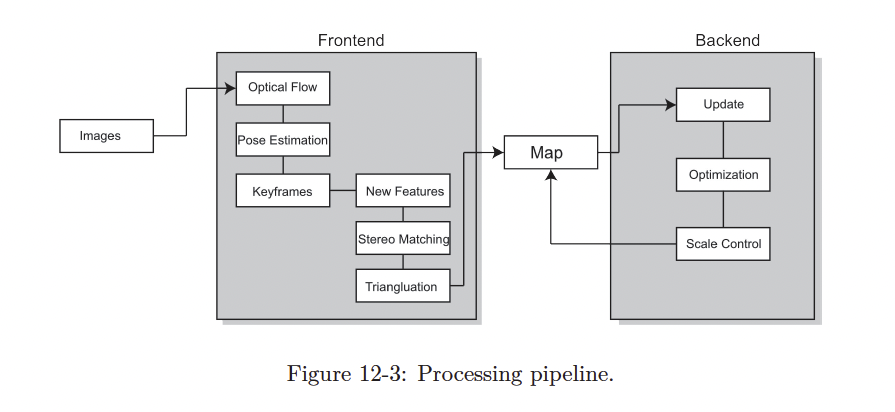
Classical Visual SLAM Stack
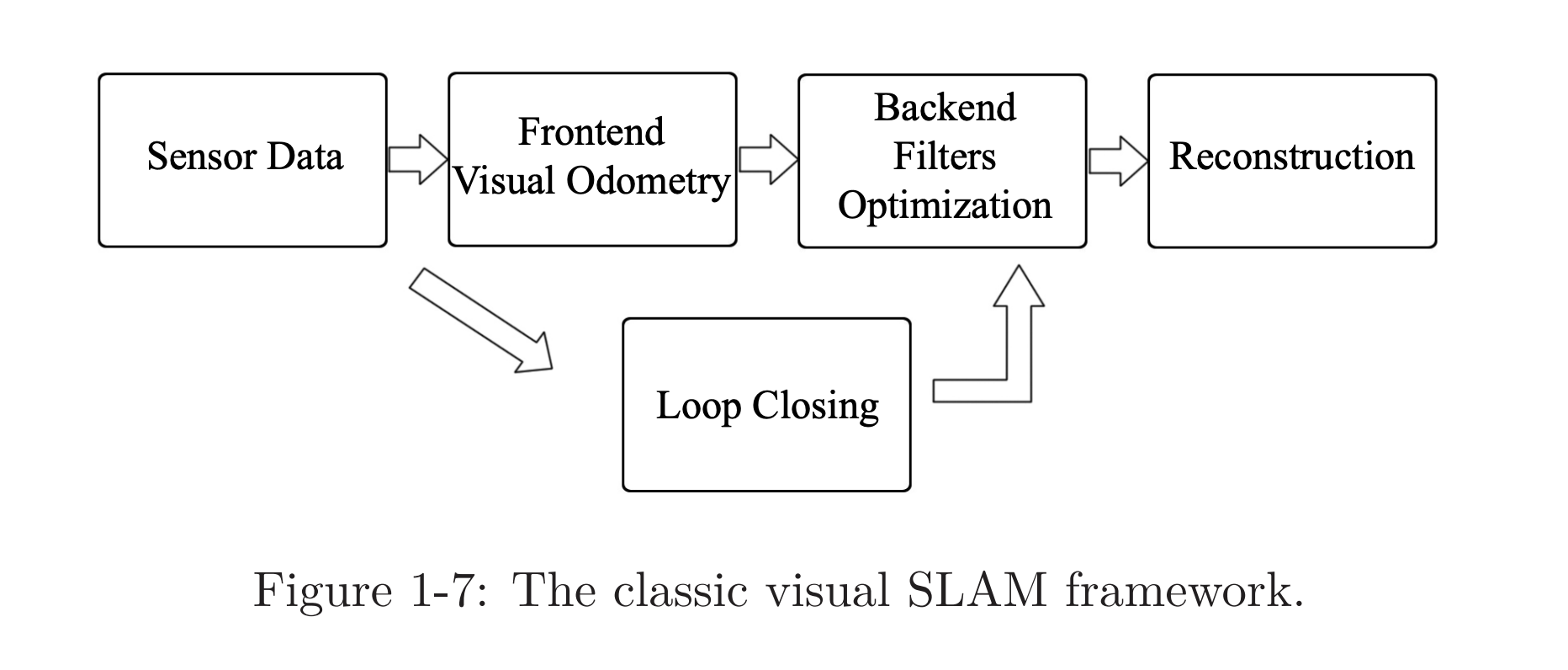
Typical Visual SLAM Workflow
A typical visual SLAM workflow includes the following steps:
- Sensor data acquisition. (cameras, and optionally motor encoders, IMUs, etc).
- Visual Odometry (frontend): VO’s task is to estimate the camera movement between adjacent frames (ego-motion) and generate a rough local map.
- Backend filtering/optimization (backend). Receives poses from VO and loop closing, and then applies optimization to generate a fully optimized trajectory and map through Bundle Adjustment
- Loop Closing. Determines whether the robot has returned to its previous position in order to reduce the accumulated drift. If a loop is detected, it will provide information to the backend for further optimization.
- Reconstruction (optional). It constructs a task-specific map based on the estimated camera trajectory.
frontend more relevant to computer vision topics (image feature extraction and matching) backend state estimation research area
Backend vs. frontend?
Like I think the frontend also does local mapping, because just calculating it over two keyframes is too noisy. So we need to window it with multiple keyframes.
SLAM Formalization
See SLAM Formalization.
Other
I think Sachin showed me this image instead